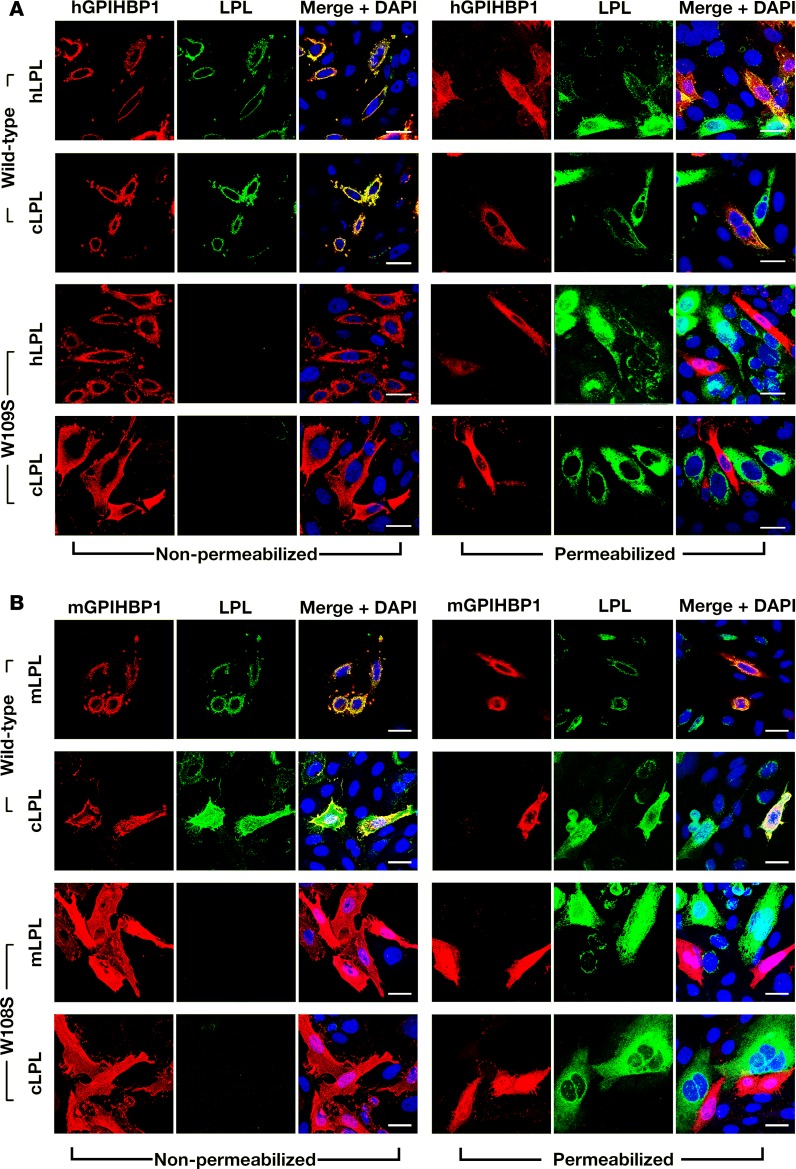
Figure 7. Chicken lipoprotein lipase (cLPL) binds to wild-type mouse GPIHBP1 (mGPIHBP1) or human GPIHBP1 (hGPIHBP1) but not to mutant GPIHBP1 proteins (mGPIHBP1-W108S, hGPIHBP1-W109S) that lack the ability to bind cLPL.
CHO pgsA-745 cells were transiently transfected with S-protein–tagged versions of wild-type or mutant GPIHBP1 and coplated with cells that had been transfected with V5-tagged versions of cLPL. Immunocytochemistry studies were performed on permeabilized and nonpermeabilized cells with a goat antibody against the S-protein tag (red) and a mouse antibody against the V5 tag (green). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). (A) Immunocytochemistry studies showing that the secreted human (hLPL) or cLPL bound avidly to neighboring CHO cells expressing wild-type hGPIHBP1 (hence, hLPL and cLPL colocalized with hGPIHBP1) but not to CHO cells expressing hGPIHBP1-W109S (no colocalization). (B) Immunocytochemistry studies showing that the secreted mouse LPL (mLPL) or cLPL bound avidly to neighboring CHO cells expressing wild-type mGPIHBP1 (colocalization) but not to CHO cells expressing mGPIHBP1-W108S (no colocalization). Scale bars: 20 μm.