Figure 4.
CCP1 cKO Cortical Invasion Phenotype Is Rescued after Birth
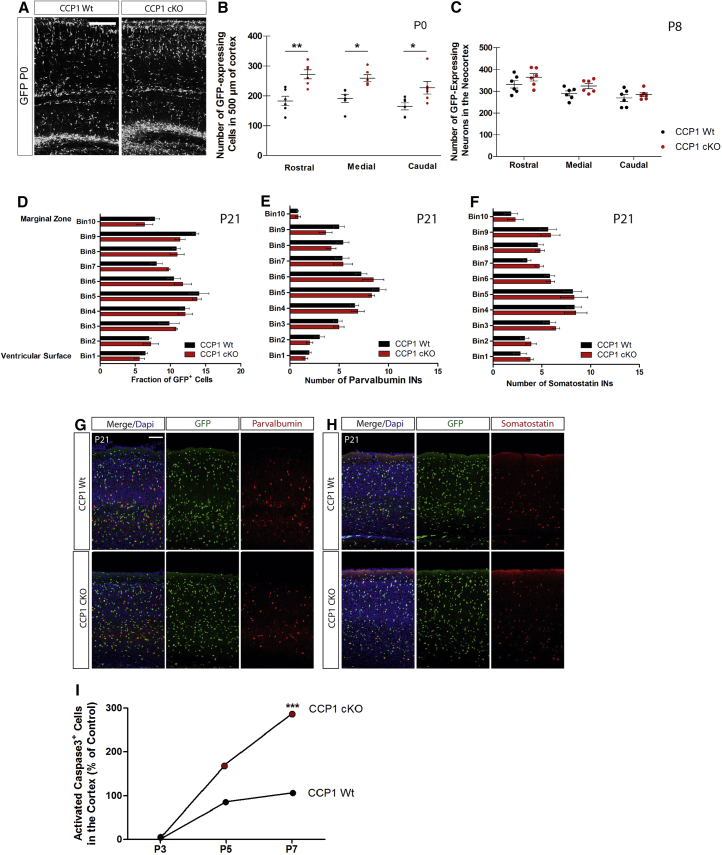
(A) Brain sections of P0 CCP1 WT and cKO animals (GFP in white).
(B and C) Number of cINs from CCP1 WT and cKO newborns at different rostro-caudal levels (n = 6 embryos from at least 3 females; two-way ANOVA, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). Scale bar, 500 μm. (B) Numbers of GFP+ cINs in rostro-caudal brain sections from CCP1 WT and cKO P8 pups (C).
(D–F) Numbers of GFP+ (D), PV+ (E), or SOM+ (F) cINs, in rostro-caudal brain sections from P21 CCP1 WT and cKO animals (n = 3–6 mice; two-way ANOVA).
(G and H) Immunolabeling showing PV+ (G) (red) or SOM+ (H) (red) expression in cINs (green) on brain sections from P21 CCP1 WT and cKO animals. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(I) Quantification of the immunoreactivity of activated caspase 3 among GFP+ cINs in brain tissue from CCP1 WT and cKO P3, P5, and P7 pups (n = 3–6 embryos from at least 3 females; two-way ANOVA, p < 0.001).
All graphs contain bars representing SEM. See also Figures S4 and S5.