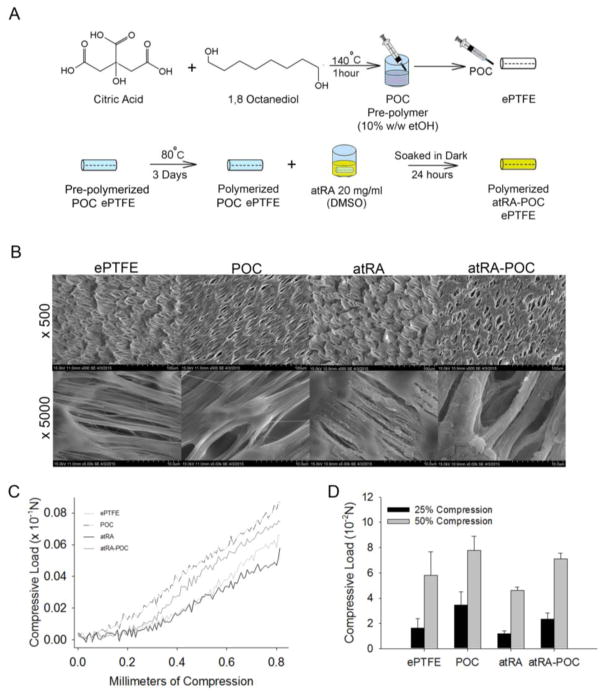
Figure 1. Synthesis and in vitro characterization of ePTFE, POC-ePTFE, atRA-ePTFE, and atRA-POC-ePTFE.
(A) Schematic of atRA-POC-ePTFE synthesis. (B) Scanning electron microscopy image of the luminal surface of ePTFE, POC-ePTFE, atRA-ePTFE and atRA-POC-ePTFE demonstrating the node and fibril structure. (C) Mechanical testing of the grafts via radial compression measurements. (D) Quantification of force required to compress each graft to 25 and 50%. Data represent the mean ± SE (n=3), analysis via one-way ANOVA. Scale bar = 20 μm, original magnification = 2.0k. ePTFE: extended polytetrafluroethylene, POC-ePTFE: poly(1,8 octamethylene citrate) ePTFE, atRA-ePTFE: all-trans retinoic acid-coated ePTFE, and atRA-POC-ePTFE: all-trans retinoic acid- poly(1,8 octamethylene citrate) ePTFE.