Table 2.
Risk loci which formed interaction peaks directly (N = 33) or via an adjacent risk locus (N = 3) with 110 target genes
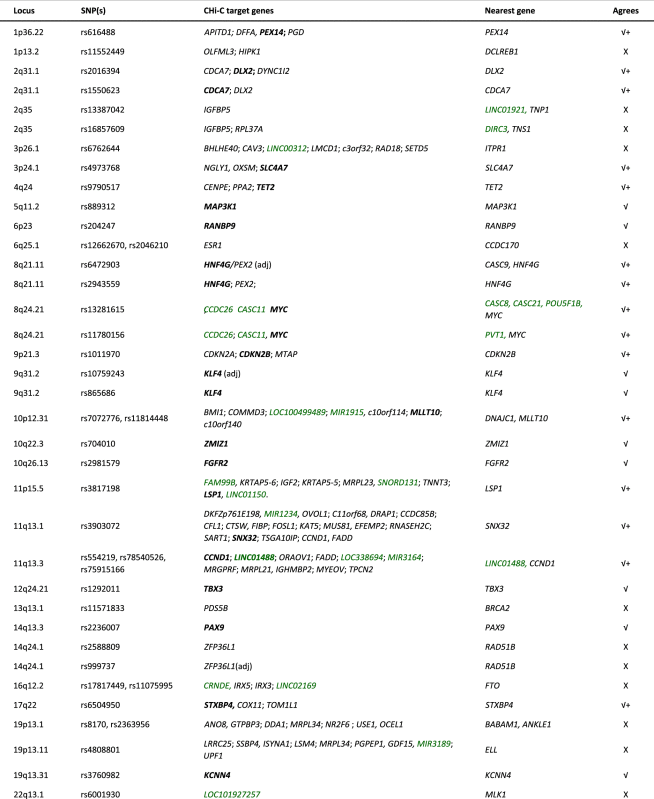
|
Where TSS for two or more target genes map to a single HindIII fragment, the genes are separated by a comma. Non-coding RNAs (long non-coding RNAs, microRNAs and small nucleolar RNAs) are indicated in green. There were three loci at which the target gene is assigned indirectly on the basis of interaction peaks with an adjacent locus; these are indicated by (adj). Defining nearest gene; for SNPs that map within a gene (UTR, exons or introns) this gene is considered to be the nearest gene, for SNPs that do not map within a gene, nearest gene is assigned based on the location of the nearest TSS according to RefSeq genes (GRCh37/hg19). Where the nearest gene is a non-coding RNA, the nearest protein-coding gene is also given. CHi-C target genes that are also the nearest gene are indicated in bold. CHi-C targets and the nearest gene are compared in the “Agrees” column; √ CHi-C data were consistent with the nearest gene being the sole target gene, √+ CHi-C data were consistent with the nearest gene being one of several target genes, X CHi-C data support a gene other than the nearest gene as a target
