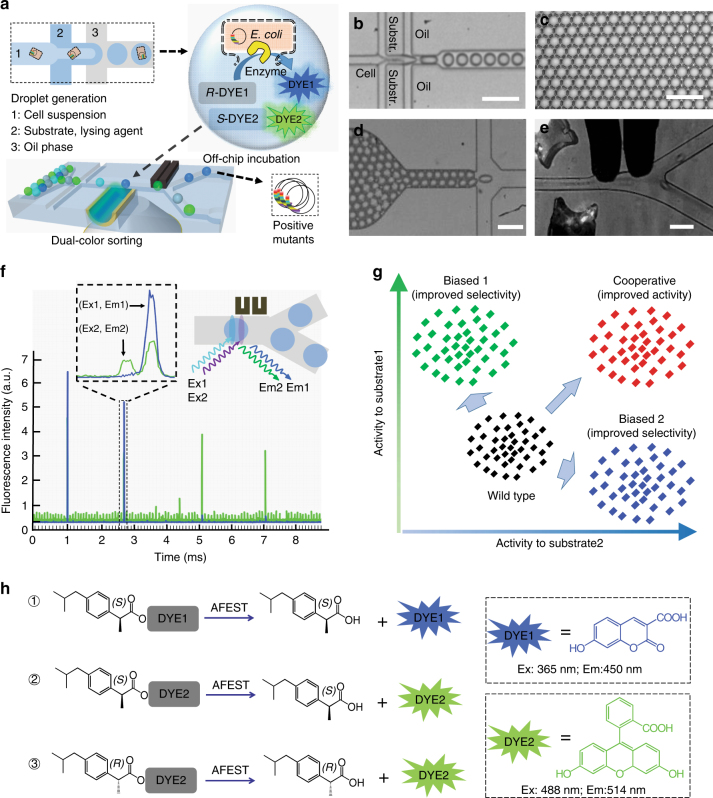
Fig. 1.
DMDS platform for screening enzymatic enantioselectivity. a Schematic of DMDS operation. Mutant enzyme-expressing single cells are encapsulated in water-in-oil droplets with two fluorogenic substrates and lysis buffer. After the droplets are incubated for a specified time, those droplets containing the desired mutants are enriched via fluorescence-activated droplet sorting. Optical images of DMDS processes: b droplet generation; c off-chip incubation; d droplet reinjection; e fluorescence-activated droplet sorting. f To avoid crosstalk of two fluorescence signals, the droplets are excited by two spatially separated lasers, which generates two temporally separated emissions. g Sorting different populations in a mutation library with the DMDS platform is achieved via two screening modes: a cooperative mode and biased modes. h Three fluorogenic substrate designs and their enzymatic reactions yielding two different fluorescence signals. Scale bars: 100 μm