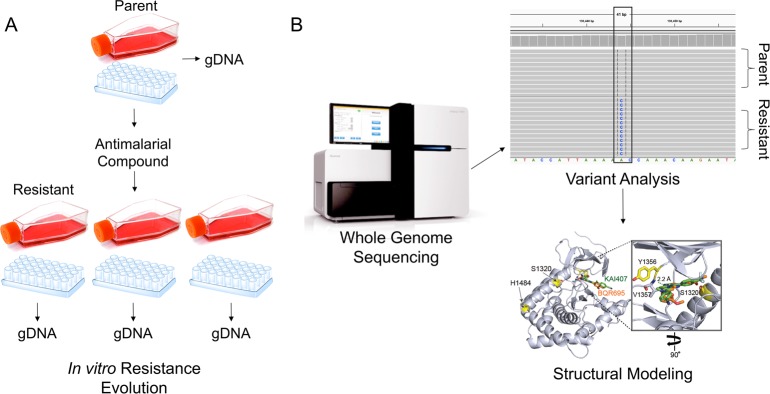
Figure 2.
Overview of IVIEWGA process. (A) A clonal aliquot (obtained by limiting dilution in a microtiter plate) of a sensitive parent P. falciparum strain is cultured in triplicate and subjected to the selective pressure of an antimalarial compound using a slow ramping or pulse method. Upon successful generation of resistant parasite bulk cultures, clones are isolated using limiting dilution and retested for resistance. (B) Whole genome sequencing is performed using gDNA extracted from the parent and resistant clones. Bioinformatic analysis calls variants between the parent and resistant lines to determine which mutations confer resistance. Generally, mutations that arise in multiple, independently derived clones are prioritized for further validation, which may include structural modeling, molecular docking simulations, and/or reverse genetics techniques.