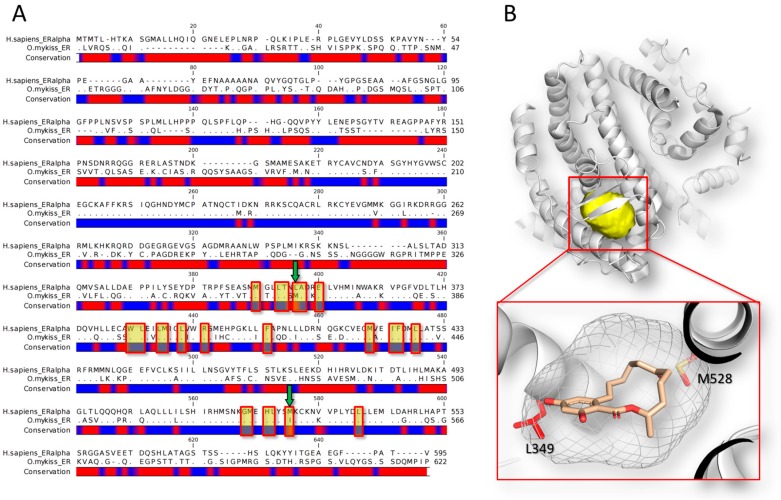
Figure 1.
Sequence and structural analysis of the human estrogen receptor alpha (Homo sapiens; GeneBank Accession number: P03372.2) in comparison to the receptor of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss; GeneBank Accession number: NP_001117821.1). (A) Sequence alignment of human (line above) and fish (line below) receptors. The alignment was done using the CLC Sequence Viewer software version 7.7 (QIAGEN, Aarhus, Denmark; https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com). Dots represent matching residues while dashes indicate gaps. The red spots in the conservation bar indicate the non-conserved regions. The residues forming the binding site are highlighted in yellow, while green arrows indicate the non-conserved residues in the binding site; (B) 3D representation of the human estrogen receptor dimer in complex with zearalenone [85]. The pictures have been obtained using the software PyMol version 1.7 (Schrödinger, New York, NY, USA; http://www.pymol.org). The protein (human estrogen receptor alpha; PDB code: 5KRC [85]) is represented in cartoon while the binding site is represented in yellow surface. The close-up in the red box shows the binding pose of zearalenone (represented in stick). The shape of the binding site is represented in white mesh, while the non-conserved residues in the fish orthologous (i.e., L349 and M528, according to the human numeration) are represented in red stick.