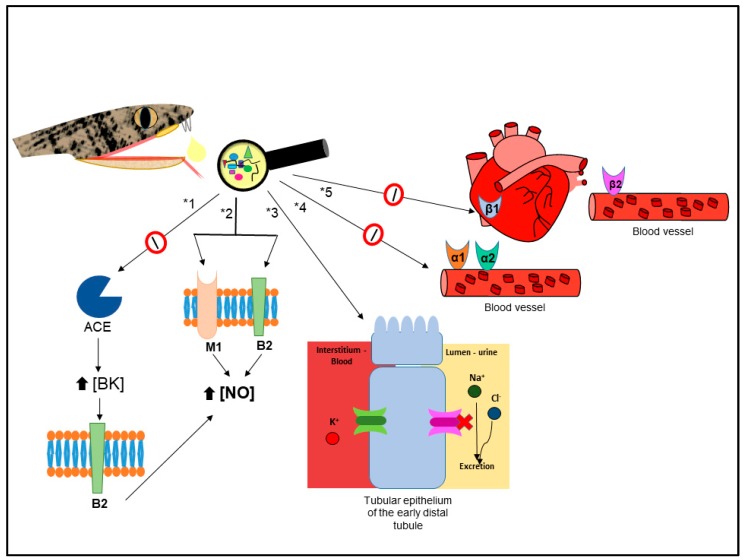
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of established and hypothesized (this work) mechanisms of action that contribute to the overall antihypertensive effect of B. jararaca venom. ACE—Angiotensin-converting enzyme; BK—bradykinin; B2—subtype 2 of bradykinin receptor; M1–subtype 1 of muscarinic receptor; NO–nitric oxide; α1—subtype 1 of the α-adrenergic receptor; α2–subtype 2 of the α-adrenergic receptor; β1—subtype 1 of the β-adrenergic receptor; β2—subtype 2 of the β-adrenergic receptor; *1—antihypertensive pathway based on [2]; *2—antihypertensive pathway based on [118]; *3 to *5—hypotheses, raised after C-map analysis, suggesting that B. jararaca venom may present: (*3) components acting similarly to thiazide/thiazide-like molecules; (*4) α-adrenergic receptor blockers; and (*5) components inhibiting both β1 and β2-adrenergic receptors contributing to the antihypertensive effect.