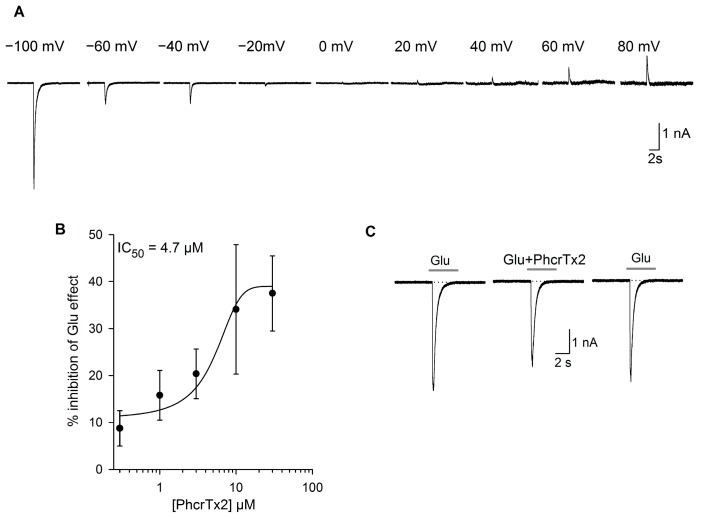
Figure 3.
Effect of PhcrTx2 on a glutamate-evoked current in isolated snail neurons. (A) Glutamate-evoked (at 1 mM of Glu) currents registered at different holding potentials (from −100 mV to +80 mV) show a current reversal at about 0 mV, indicating that it most probably is a non-selective cation permeant channel; (B) Concentration-response relationship of the inhibitory effect of PhcrTx2 on glutamate-gated currents. Data were fitted by a dose-response function with an IC50 of 4.7 µM. Each point represents the mean ± SE from four to seven neurons; (C) Representative current traces elicited by glutamate (1 mM) under control condition, in the presence of 30 µM PhcrTx2, and after washout of the toxin.