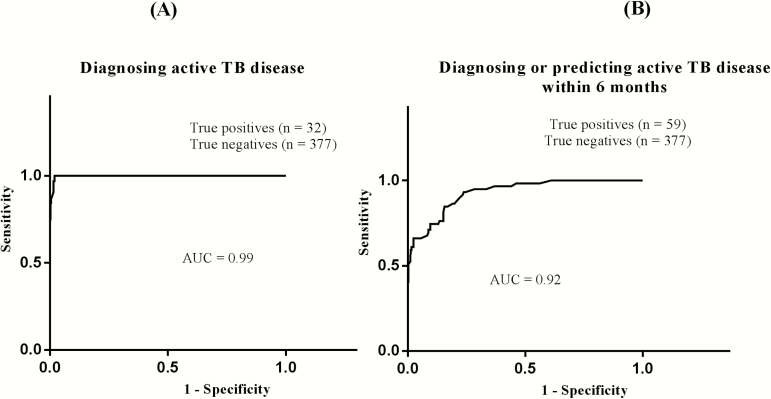
Figure 4.
Receiver operating characteristic curves for the use of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity in diagnosing (A) and predicting (B) active tuberculosis disease in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A, Using a cutoff of 0.80, plasma IDO activity had a diagnostic sensitivity of 97.0% (confidence interval, 83%–99%) and a specificity of 98.9% (96%–99%; Supplementary Table S1). B, For predicting active tuberculosis disease within 6 months, using the same cutoff, IDO activity had a sensitivity of 61% (confidence interval, 42%–68%) and a specificity of 99% (97%–99%; Supplementary Table S3). Patients with active tuberculosis were combined with those who went on to develop tuberculosis because pragmatically the whole group could potentially benefit from antituberculosis therapy. (For similar analysis excluding time of tuberculosis diagnosis, see Supplementary Table S4.) AUC, area under the curve; TB, tuberculosis.