Figure 1. Complement activation and regulation.
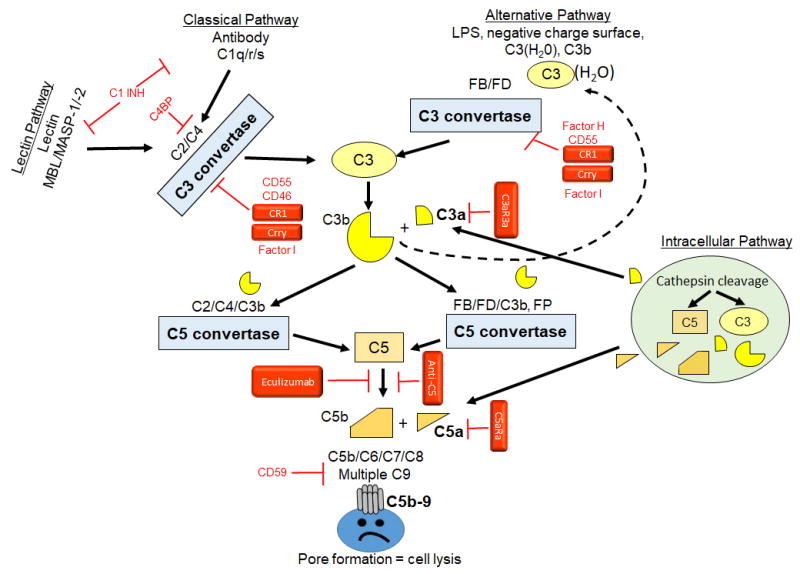
Classical pathway of complement activation initiates with antibody binding and recognition by the C1q/r/s complex to cleave C2 and C4 to form a C3 convertase (C2aC4b; blue box). Lectin pathway of complement activation initiates with Mannose Binding Lectin (MBL) recognition of lectins on the cell surface and subsequent activation of MASP-1 and MASP-2. The MBL/MASP-1/-2 complex also activates C2 and C4 forming the same C3 convertase as the classical pathway. The alternative pathway is initiated by multiple substances including negatively charged surfaces, pattern recognition molecules such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and a spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 to form C3(H2O). The alternative pathway C3 convertase forms when Factor D cleaves Factor B bound C3b to form C3bBb. Both C3 convertases cleave C3 to form C3b and release anaphylatoxin C3a. C3b may also initiate the alternative pathway leading to amplification of the complement response (dashed line). C3b is added to each convertase forming the C5 convertase. C5 convertases cleave C5 to C5b to initiate the common terminal pathway resulting in C5b-9 assembling as the membrane attack complex pore in the cell surface and resultant cell lysis. The intracellular pathway includes Cathepsin cleavage of C3 or C5 allowing C3a or C5a, respectively to bind appropriate receptors either on intracellular or extracellular membranes. Regulators indicated in red include classical initiation inhibitors, C1INH which inhibits the formation of both C1q/r/s and MBL/MASP-1/-2 and the C4b Binding Protein (C4BP) which inhibits C4 cleavage. The classical C3 convertase is inhibited by multiple proteins including CD55 (Decay accelerating factor, DAF), CD46 (Membrane Cofactor of Proteolysis, MCP), CR1 (Complement receptor 1), Crry (Complement receptor 1 related protein Y, rodents only). The alternative C3 convertase inhibitors include Factor H, CD55, CR1 and Crry. CD46, Factor H, CR1 and CRRY induce Factor I activity to degrade C3b and C4b. CD59 (Protectin) inhibits C5b-9 formation. Therapeutic compounds used in either animal or human studies are indicated in Red boxes. These agents inhibit C3 convertase activity (sCR1, Crry), bind C5 (Eculizumab or anti-C5) or antagonize the C3aR or C5aR1 (C3aRa or C5aRa)
