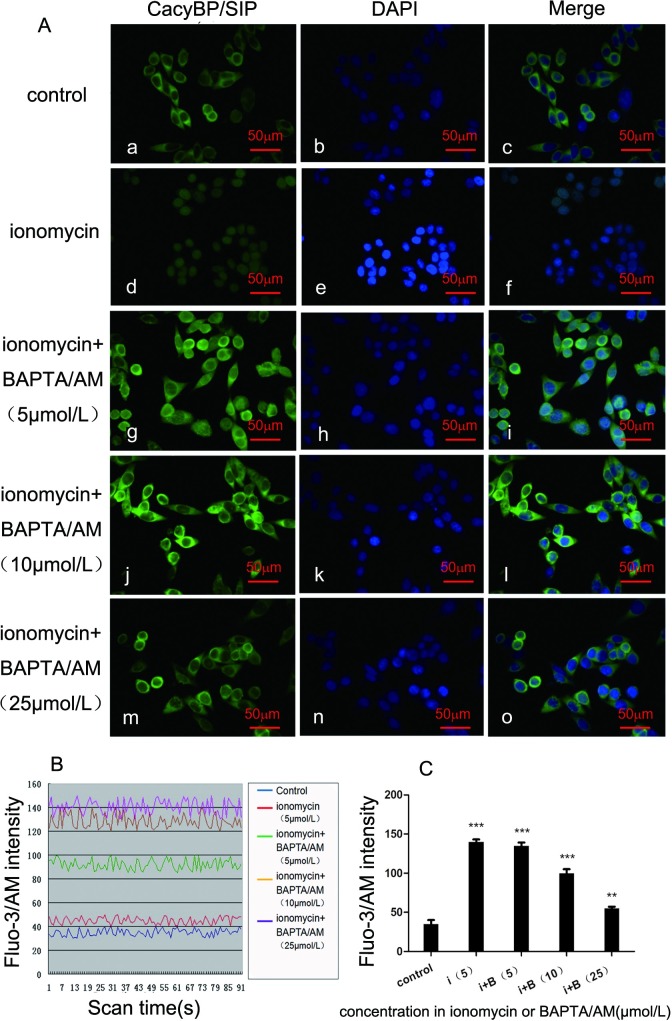
Fig 2. The effect BAPTA/AM on the nuclear localization of CacyBP/SIP induced by ionomycin in SW480 cells.
(A) Effect of BAPTA/AM on ionomycin-stimulated nuclear translocation of endogenous CacyBP/SIP. Cells were treated with 5 μmol/L of ionomycin plus different concentrations of BAPTA/AM (0, 5, 10, and 25 μmol/L) for 30 min, followed by immunostaining using anti-CacyBP/SIP, and were imaged with confocal microscopy. Effect of different concentrations of ionomycin on the localization of endogenous CacyBP/SIP. SW480 cells were fixed and immunostained using CacyBP/SIP MAb (panels a, d, g, j, and m); nuclei were labeled with DAPI (panels b, e, h, k, and n). The merged images are shown in panels c, f, i, l, and o. The scale bar represents 50 μm. (B) The intensity of cytosolic free intracellular Ca2+ fluorescence stimulated by 5 μmol/L of ionomycin plus different concentrations of BAPTA/AM (0, 5, 10, and 25 μmol/L) in SW480 cells. BAPTA/AM at concentrations of 10 μmol/L and 25 μmol/L totally abolished the nuclear translocation of CacyBP/SIP induced by 5 μmol/L of ionomycin. Cells were loaded with 20 μmol/L of Fluo-3/AM for 45 min under a confocal microscope (495 nm). The fluorescence was captured every 2 sec and recorded for 3 min. (C) The bar chart shows the intracellular Fluo-3 intensity. The Fluo-3 fluorescence intensity was reduced by 5 μmol/L of ionomycin plus 10 μmol/L and 25 μmol/L of BAPTA/AM. Error bars represent the mean±s.d.