Figure 5.
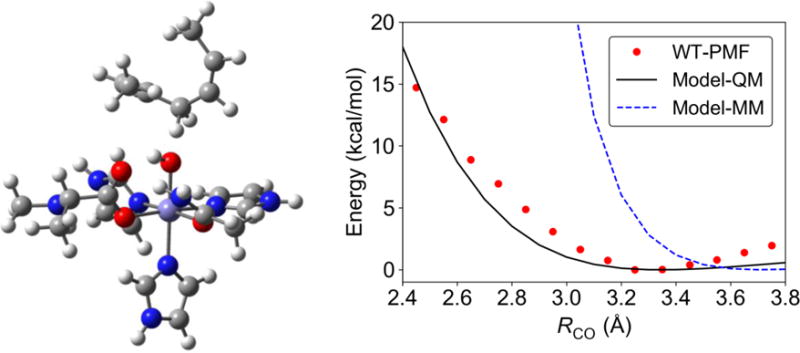
Gas phase model (left) used to probe the energy along RCO with QM and MM methods (right). The energies were computed with a rigid body scan, starting with the transition state geometry for this complex and retaining the geometries of the individual substrate and Fe complex components as RCO is changed. The QM energy was obtained at the B3LYP/6-31G** level of theory, and the MM energy was obtained with the AMBER force field with extensions (see SI). For comparison, the PMF, which corresponds to free energy, for the WT SLO obtained with QM/MM free energy simulations is also depicted in this figure. Additional rigid scans for the gas phase model obtained with different QM levels of theory at each value of RCO, as well as scans with smaller gas phase models, are provided in the SI (Figures S6 and S7). These QM calculations were performed using Gaussian 09, Revision D.01.55
