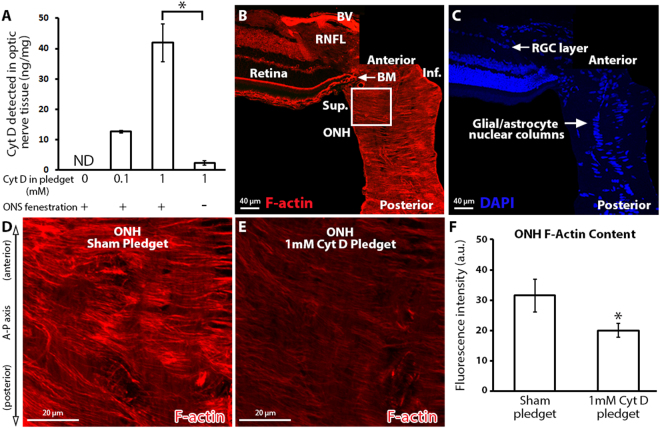
Figure 1.
The effect of local cytochalasin D delivery on optic nerve head filamentous actin content. (A) Total Cyt D (ng) detected in the anterior 2 mm of optic nerve after surgical delivery, normalized to the total protein (mg) content of the anterior 2 mm optic nerve per animal. Note the significant reduction in Cyt D delivery to the optic nerve in the absence of optic nerve sheath fenestration (n = 2, 2, 3, 3 from left to right). (B,C) Montage of normal anterior optic nerve and superior retina, labeled with fluorescent-labeled phalloidin (filamentous actin maker) and DAPI (nuclear maker). The superior ONH is identified by the white box. (D,E) ONH after sham (pledget soaked in vehicle only) delivery and 1 mM Cyt D delivery to the junction of the superior optic nerve and globe. (F) ONH F-actin content assessed by fluorescence intensity measurement of fluorescent-labeled phalloidin after sham (n = 4) and 1 mM Cyt D delivery (n = 6). *p < 0.05. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. A–P = anterior-posterior; a.u. = arbitrary units; BM = Bruch’s membrane; BV = blood vessel; Cyt D = cytochalasin D; F-actin = filamentous actin; Inf. = inferior; ND = none detected; ONH = optic nerve head; ONS = optic nerve sheath; RGC = retinal ganglion cell layer; RNFL = retinal nerve fiber layer; Sup. = superior.