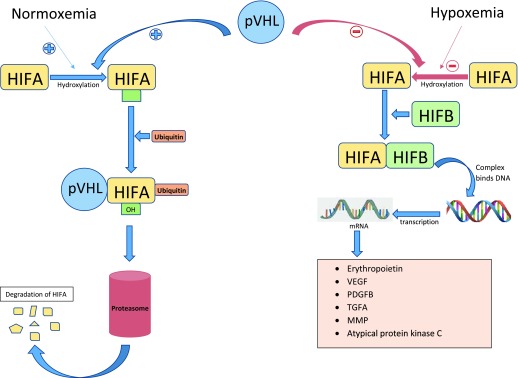
Figure 1. VHL/HIF axis.
Under normal oxygen tension, HIF1A and HIF2A are hydroxylated on proline residues and bind the pVHL, resulting in the polyubiquitination of HIFA, which targets it for proteasomal degradation. Under conditions of hypoxemia or in the absence of pVHL, hydroxylation of HIF1A and HIF2A does not occur and HIFA accumulates and dimerizes with HIFB and acts as a transcription factor, resulting in increased mRNA levels coding for VEGF, PDGFB, TGFA, erythropoietin, and extracellular matrix protein. HIFA, hypoxia-inducible factor alpha; HIFB, hypoxia-inducible factor beta; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase protein; mRNA, messenger RNA; PDGFB, platelet-derived growth factor beta; pVHL, protein of Von Hippel–Lindau gene; TGFA, transforming growth factor alpha; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.