Figure 3.
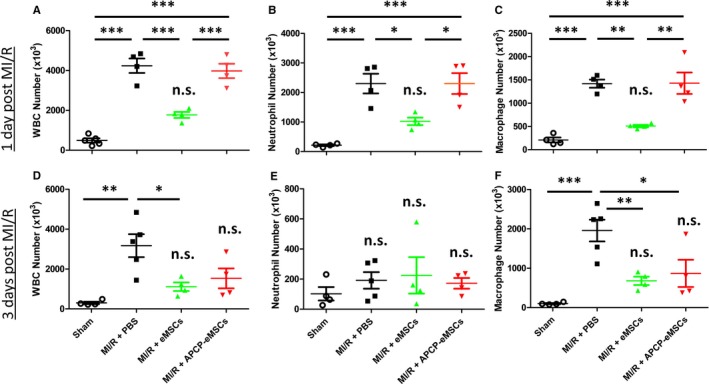
Implantation of eMSCs reduces infiltration of innate immune cells at 1 and 3 days after myocardial MI/R injury. Quantification of innate immune cell subtypes by flow cytometry in animals treated with PBS, eMSCs, or APCP‐eMSC. Animals treated with eMSCs had significantly reduced infiltration of (A) CD45+ WBCs, (B) MPO high neutrophils, and (C) CD68high macrophages compared with PBS 1 day following injury. Animals treated with APCP‐eMSCs had no significant reduction of any cell type quantified compared with PBS control 1 day after injury. Implantation of eMSCs also lead to sustained reduction in overall (D) CD45+ WBC infiltration compared with PBS‐treated controls 3 days after MI/R injury. None of the treatment groups had significantly different (E) MPO high neutrophil infiltration compared with sham injury at 3 days. F, CD68high macrophage infiltration was significantly reduced by eMSC‐treated animals compared with PBS control. APCP‐eMSC‐treated animals also did not demonstrate significant differences compared with sham at 3 days following injury. Data are expressed as mean±SEM, n=4 to 5, *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005, n.s. indicates not significant compared with sham. One‐way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc test. APCP‐eMSCs indicates α,β‐methylene adenosine diphosphate pretreated eMSCs; eMSCs, encapsulated mesenchymal stromal cells; MI/R, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PBS, phosphate‐buffered saline; WBCs, white blood cells.
