Figure 2.
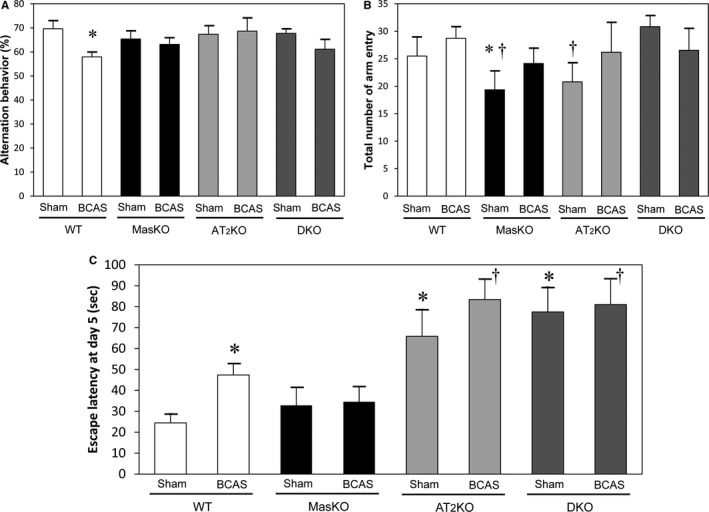
Cognitive function. Working memory and spontaneous locomotive activity in mouse groups determined with Y‐maze test. A, The percentage of alternation behavior is used to estimate working memory. Working memory was significantly reduced in wild‐type mice (WT) after bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS) but not in the other groups (n=8–14 for each group). B, Spontaneous locomotive activity is defined as the total number of arm entries. Mas receptor knockout mice (MasKO)–sham and angiotensin II type 2 receptor knockout mice (AT2KO) showed significantly lower locomotive activity compared with WT and Mas/AT2KO (DKO) (n=7–15 for each group). *P<0.05 vs WT‐sham. † P<0.05 vs DKO‐sham. C, Escape latency of the Morris water maze test on the last day was significantly longer in WT‐BCAS than in WT‐sham. AT2KO‐sham and DKO‐sham mice showed markedly longer latency compared with WT and MasKO (n=8–22 for each group). *P<0.05 vs WT‐sham. † P<0.05 vs WT‐BCAS.
