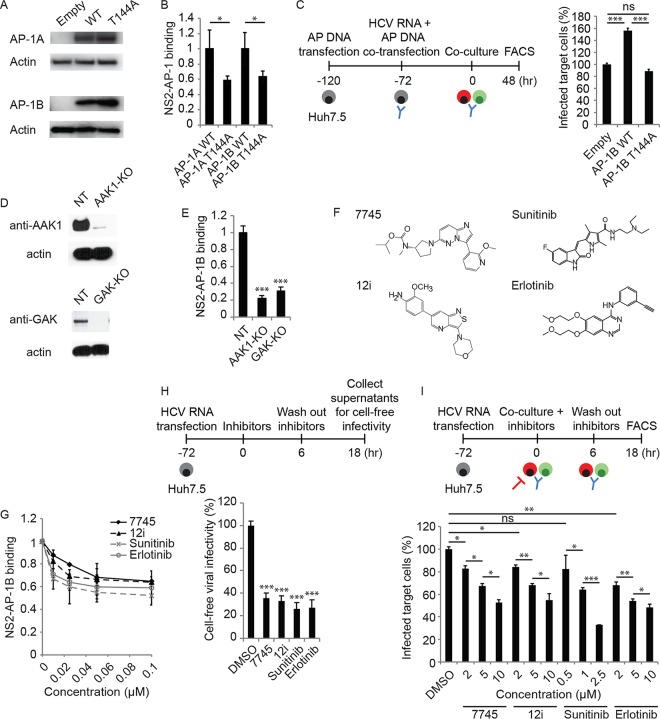
FIG 6 .
AAK1 and GAK regulate NS2–AP-1 binding and HCV cell-free and cell-to-cell spread. (A) AP-1 expression following transfection of Huh7.5 cells with GLuc-tagged WT or T144A mutant AP-1A/B or an empty control and blotting with anti-GLuc and anti-actin antibodies. (B) NS2 binding to WT and T144A mutant AP-1A/B measured by PCA. Data are plotted relative to the respective WT control. (C) HCV cell-to-cell spread in AP-1B-overexpressing cells versus an empty-vector control measured via FACS analysis 48 h following coculturing of HCV RNA-transfected donor Huh7.5 cells with GFP-expressing target cells. (D) Confirmation of gene expression knockout (KO) by Western blotting in Huh7.5 cells transduced with CRISPR subgenomic RNA lentivirus targeting AAK1 or GAK or an NT control. (E) NS2 binding to AP-1B measured in AAK1 and GAK knockout cells by PCAs. Data are plotted relative to the control cells. (F) Chemical structures of the compounds indicated. (G) Effects of the compounds indicated on NS2–AP-1B binding measured by PCA. (H) Cell-free infectivity of culture supernatants collected following a 6-h treatment of HCV RNA-transfected cells with the four individual compounds at a concentration of 10 μM (compound 7745, 12i, and erlotinib) or 2.5 μM (sunitinib), followed by compound removal and a 12-h incubation in fresh medium, measured via luciferase assay at 72 h postinoculation of naive cells. (I) Dose response of HCV cell-to-cell spread to the compounds indicated measured by FACS analysis following a 6-h treatment of cocultures of HCV RNA-transfected Huh7.5 donor cells and GFP-expressing target cells. Shown in panels B, C, E, and G to I are representative results of experiments from at least two conducted, each with three to six biological replicates. Shown are the mean ± SD. ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (relative to WT AP-1 [B] or an empty-vector [C], NT [E], or vehicle [G to I] control; two-tailed unpaired t test [B], one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s [C] or Dunnett’s [E, H, and I] post hoc test).