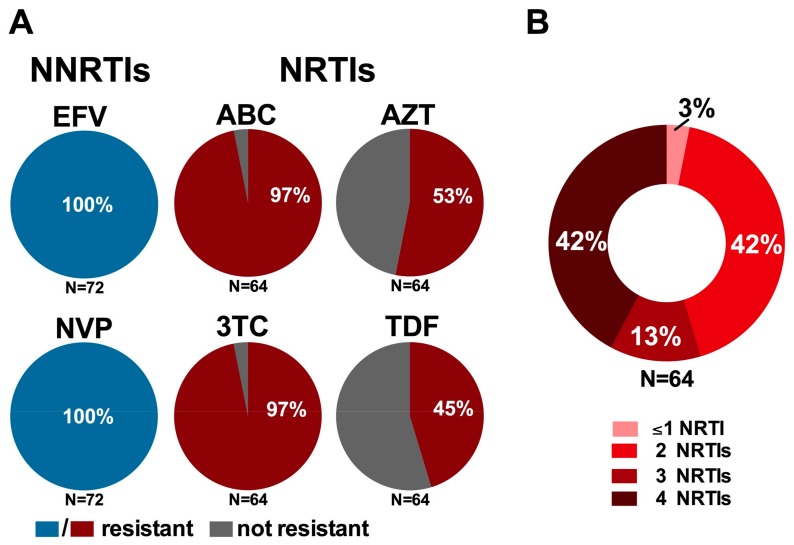
Figure 3.
Implications of resistant genotypes on recommended first- and second-line regimens: (A) prevalence of resistance to recommended first-line NNRTIs (blue) and NRTIs (red) among participants harboring NNRTI (N = 72) and NRTI (N = 64) resistance, respectively; and (B) burden of multi-NRTI resistance among participants harboring NRTI resistance (N = 64). Resistance to individual drugs was defined using the Stanford Drug Resistance Database, where genotypes exhibiting any level of reduced susceptibility to a given drug were considered “resistant” [51,52].