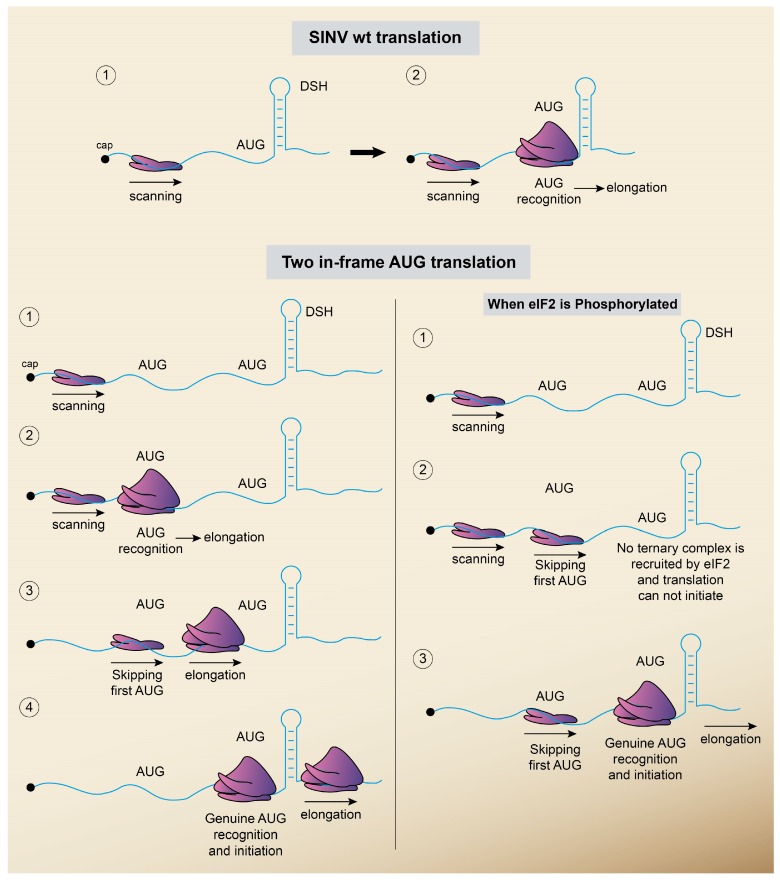
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the model for the initiation of translation on SINV sgRNA. (Upper panel) In the model of the scanning mechanism followed by WT SINV sgRNA to initiate translation, the 40S ribosomal subunit attaches initially at the 5′ cap structure. Then, the 5′ UTR is scanned base-by-base in a 5′–3′ direction until the initiation codon (AUG) is recognized. (Lower panel) Model for translation initiation on SINV sgRNA bearing two alternative start codons (AUG). Under no stress conditions (left part), the preinitiation complex containing the 40S ribosomal subunit interacts with the cap structure and scans the leader sequence of sgRNA until the first AUG is encountered. Then, the 80S initiation complex can be formed and elongation ensues. Another preinitiation complexes can start scanning from the cap structure and, in some cases, skip the first AUG start codon and reach the second AUG (genuine AUG), initiating the synthesis of authentic C protein from this start codon. When eIF2 is phosphorylated (right part), the lack of functional eIF2 prevents the initiation in the first AUG, nevertheless the genuine AUG, which is in proximity with DSH, manages to initiate the translation independently of the eIF2.