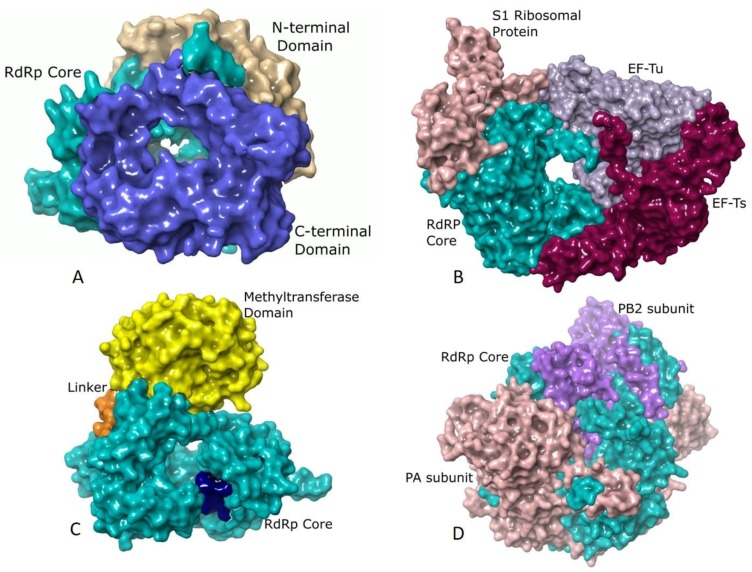
Figure 2.
Additional structural elements of different RdRps: (A) The surface representation of RdRp of Mammalian orthoreovirus 3 (MRV3) (PDB ID: 1n35) [29] showing the core (residues 371–890, colored turquoise) in association with the C-terminal bracelet domain (shown in blue) composed of residues 891–1267 and the N-terminal domain (depicted in tan) spanning residues 1–370. While the N-terminal domain restricts the movements of the thumb and fingers subdomains, the C-terminal domain resembles the sliding clamp of DNA polymerases in structure and has a positively charged opening of 20 Å diameter. (B) Qβ polymerase (PDB ID: 4r71) [72] shown in surface representation with the core RdRp (β-subunit, Chain B, residues 1–571) colored turquoise, host translation elongation factors EF-Tu (Chain A, residues 2–1393, colored mauve) and EF-Ts (Chain C, residues 4–1394, colored dark magenta) and the S1 ribosomal protein (Chain E, residues 1–171, colored rosy brown). The extensive interactions of EF-Tu with the β-subunit is believed to aid in rapid separation of the duplex RNA that is formed during polymerization thereby allowing exponential amplification of phage genome. The S1 protein is involved in recognizing (+) strand of Qβ [72]. (C) The RdRp of Dengue virus (DENV) (PDB ID: 4hhj) [73] rendered in surface showing the core (residues 272–900, colored turquoise) with the priming loop residues 789–805 shown in dark blue, the methyltransferase domain (residues 1–262) in yellow and the linker (residues 213–271) in orange. The methyltransferase domain is an essential part of the replication machinery that catalyzes 5’-RNA capping and methylation during viral genome replication. (D) The Influenza B virus (FluB) replicase (PDB ID: 4wrt) [50] consists of the PA (Chain A, residues 1–726, colored sandy brown), PB1 (Chain B, residues 1–752, colored turquoise) and PB2 (Chain C, residues 1–770, colored purple) domains are shown in surface representation. PB1 has polymerase activity, PB2 possesses a cap-binding domain and PA contains an endonuclease domain. The PA and PB2 domains lie towards the N- and C-terminal domains of PB1, respectively.