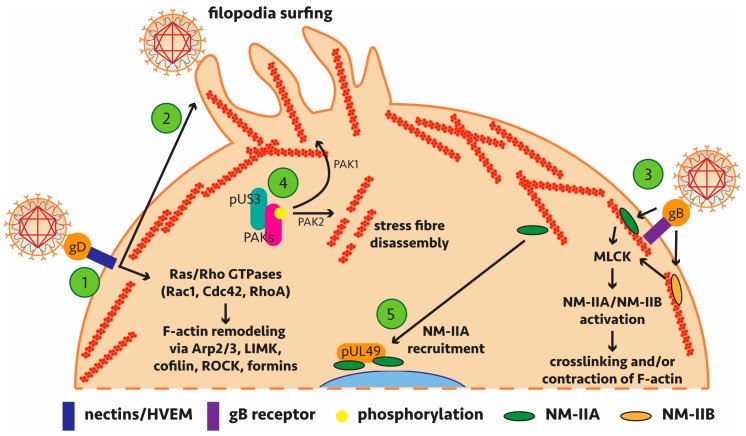
Figure 2.
Identified alphaherpesvirus-host interactions involved in actin remodelling or myosin recruitment. This schematic highlights the findings of Table 1 and Table 2, representing the known specific interactions and pathways involved in alphaherpesviral regulation of actin dynamics. 1: Viral envelope glycoprotein gD binds nectins and/or the herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) to activate Ras/Rho GTPases. This triggers actin remodelling via the Arp2/3 complex, LIM domain kinases (LIMK), cofilin, Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) and formins. 2: gD binding to surface receptors can trigger the formation of filopodia. The virus can associate with these and undergo “surfing” to bring the virus closer to the main body of the cell for entry. 3: Non-muscle myosins, NM-IIA and NM-IIB, can act as entry coreceptors for viral envelope glycoprotein gB, activated by upstream myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) activation, leading to remodelling of F-actin. 4: Viral kinase pUS3 phosphorylation of the p21-activated kinases (PAKs) can lead to formation of protrusions (PAK1) and stress fibre disassembly (PAK2). 5: Viral protein pUL49 can sequester a subpopulation of NM-IIA at the perinuclear space which may rearrange actin for viral nuclear egress.