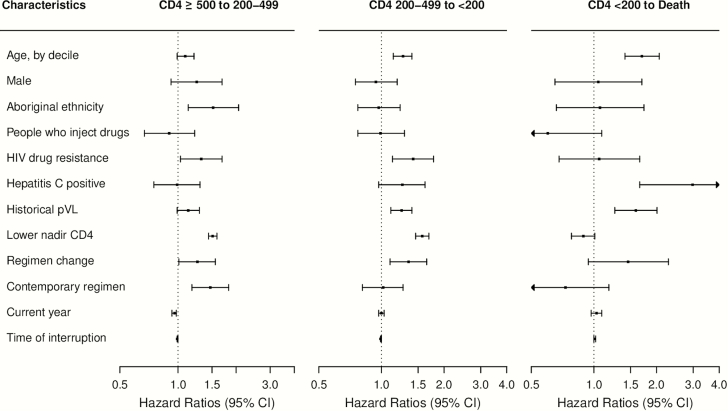
Figure 3.
Adjusted hazard ratios associated with disease state transition intensities during the first antiretroviral therapy (ART) interruption episode among 2212 individuals. Four-state Markov models estimated the baseline transition intensities for each of the 5 possible transitions (CD4 count [cells/μL] ≥500 to 200–499; 200–499 to <200; ≥500 to death; 200–499 to death; and <200 to death); covariate effects of the 2 transitions (≥500 to death; and 200–499 to death) was not estimated due to the small observed transition number; results of the missing categories of the covariates were not shown. HIV drug resistance was considered as nonreversible, and determined as detecting mutations based on a modification of the 2014 International AIDS Society–USA mutation list. Historical plasma viral load (pVL) was measured as area under the pVL curve prior to ART interruption. Modern (contemporary) regimens included those based on lamivudine + tenofovir or emtricitabine + tenfovir combined with efavirenz, rilpivirine, or etravirine or a boosted protease inhibitor or integrase inhibitor regimen; small numbers of individuals could have received tipranavir, maraviroc, or enfuvirtide. Time of interruption was measured by time from ART initiation to interruption in months. Abbreviations: ART, antiretroviral therapy; CI, confidence interval; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; lower nadir CD4, lowest CD4 cell count prior to antiretroviral therapy interruption, per 100 cells/μL decline; pVL, plasma viral load.