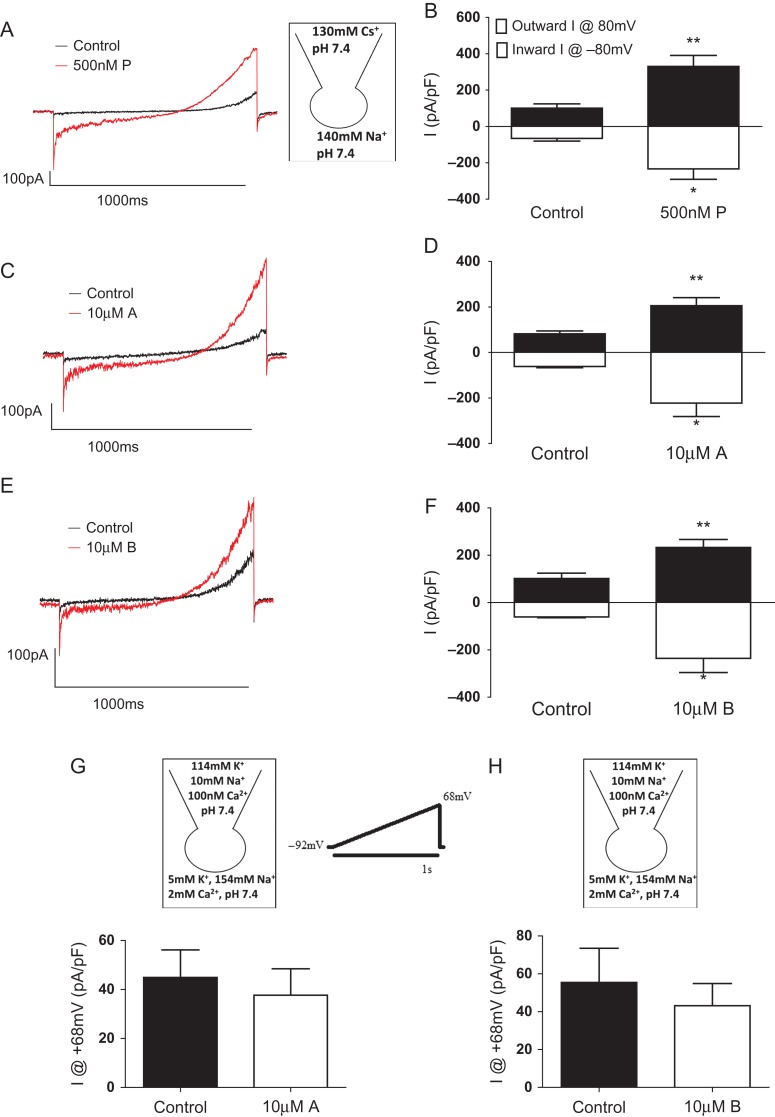
Figure 5.
Patch-clamp electrophysiology. Compounds A and B selectively potentiate CatSper currents. Monovalent (NaDVF) CatSper currents (ICatSper) were evoked by ramp depolarization from −80 mV to 80 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV. (A) An example recording of 500 nM progesterone (P) potentiation of ICatSper. (B) Quantification of progesterone-induced potentiation of maximum inward and outward ICatSper (n = 4). (C) An example recording of 10 μM compound A potentiation of ICatSper. (D) Quantification of A-induced potentiation of maximum inward and outward ICatSper (n = 4). (E) An example recording of 10 μM compound B-induced potentiation of ICatSper. (F) Quantification of B-induced potentiation of maximum inward and outward ICatSper (n = 5). K+ currents were recorded under quasi-physiological conditions and evoked by ramp depolarization from −92 to 68 mV from a holding potential of −92 mV (voltage protocol shown). Neither compound A (n = 4) nor B (n = 4) altered K+ current (measured at 68 mV, the Na+ reversal potential; G, H).