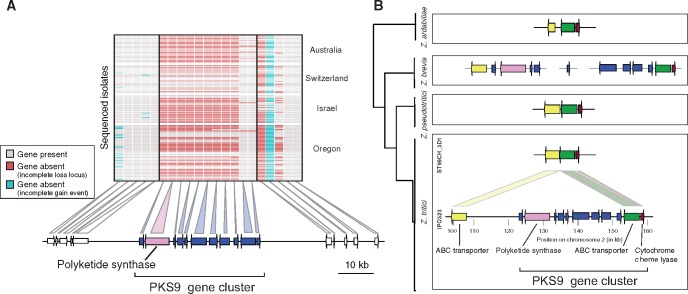
Fig. 4.
Evolution of the polyketide synthase (PKS) 9 gene cluster in Zymoseptoria tritici and the sister species Z. pseudotritici, Z. brevis, and Z. ardabiliae. (A) Gene presence–absence polymorphism affecting the PKS9 gene cluster among the 123 Z. tritici isolates grouped by population. The physical position of each gene is shown below. (B) Comparative genomics analyses of the PKS9 gene cluster in Z. tritici and the three closest known sister species Z. pseudotritici, Z. brevis, and Z. ardabiliae. On the left is a schematic tree representing the phylogenetic relationships between Z. tritici and three sister species. In Z. tritici, two segregating variants of the PKS9 gene cluster were found. Isolate ST99CH_3D1 is lacking nearly all genes of the PKS9 cluster compared with the IPO323 reference genome. Analyses of the homologous regions in five Z. pseudotritici and four Z. ardabiliae genomes showed that the gene cluster was missing with the exception of two genes encoding an ABC transporter and a cytochrome c heme lyase, respectively. In Z. brevis, all genes of the PKS9 cluster were present, however orthologs were split on three different genome assembly scaffolds.