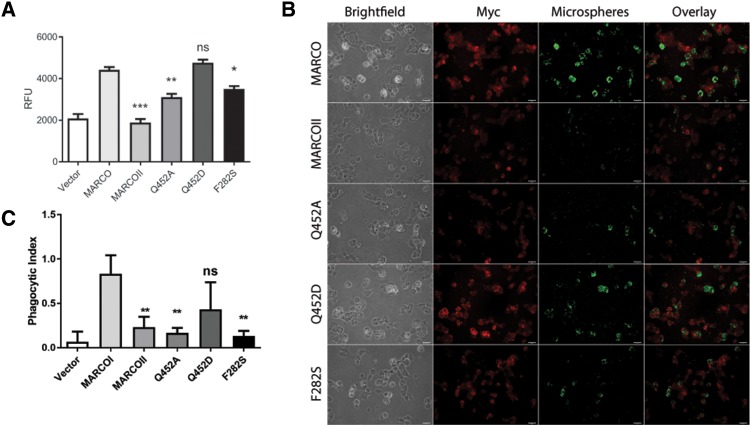
Fig. 5.
Residues at positions 452 and 282 of MARCO influence ligand association and bacterial internalization. (A) Mutation of glutamine residue 452 to alanine (Q452A) reduces ligand-coated microsphere association in HEK 293 T cells, whereas mutation to the ancestral aspartic acid (Q452D) does not. Mutation of residue phenylalanine 282 to the ancestral serine (F282S) also reduces microsphere association. Statistical comparisons relative to MARCO were made using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Experiments were performed a minimum of three times with a minimum of three technical replicates. (B) Immunofluorescence microscopy of microsphere association in HEK 293 T transfected with empty vector, MARCO, MARCOII, or variants Q452A, Q452D, and F282S. Scale bars represent 25 µm. (C) Mutation of residue 452 to alanine (Q452A) or residue 282 to serine (F282S) greatly reduces the phagocytic index of RAW 264.7 macrophages. Phagocytic index was calculated as number of internalized bacteria divided by the number of RAW 264.7 macrophages counted. Statistical comparisons relative to MARCO were made using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01.