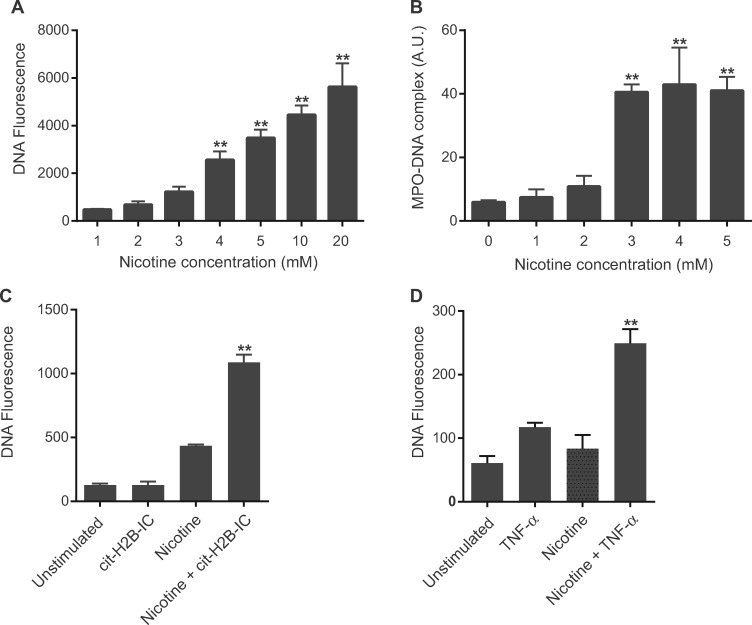
Fig. 2.
Nicotine induces NETosis in neutrophils from healthy non-smokers
(A) and (B) Nicotine induced NETosis in neutrophils in a dose-dependent manner as measured by the fluorescent intensity of SYTOX green (A; **P < 0.0001 vs 1 mM nicotine) as well as by NET-specific MPO–DNA complex ELISA (B; **P < 0.0001 vs 0 mM nicotine). (C) Cit-H2B IC and nicotine have a synergistic effect on neutrophil NETosis (**P < 0.001 vs cit-H2B IC or 1 mM nicotine). (D) TNF-α primes neutrophils to undergo NETosis at a lower concentration of nicotine (1 mM; **P < 0.005 vs TNF-α or nicotine). Bars represent the mean (s.e.m.). Cit-H2B IC: citrullinated H2B immune complexes; MPO-DNA: MPO–DNA complexes.