Fig. 5.
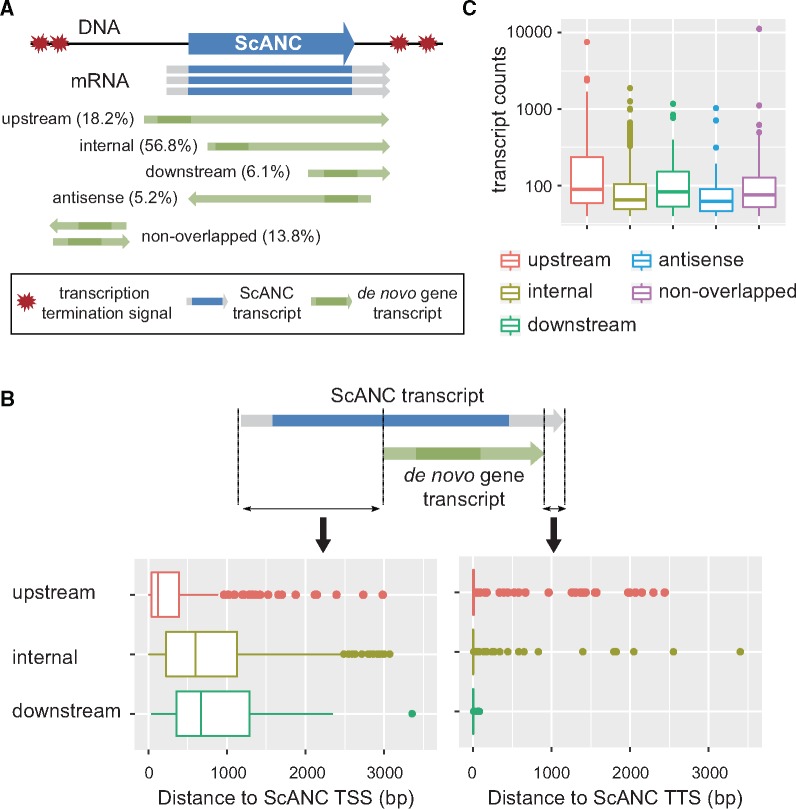
Transcript structures of de novo genes are often affected by ScANCs. (A) De novo genes whose transcripts are in the same direction and overlap with that of an associated ScANC were further classified into “upstream,” “internal,” or “downstream” types depending on the relative positions of their initiation and stop codons with respect to that of the associated ScANC. The darker regions of the transcripts correspond to CDSs. Only de novo genes with >40 transcripts in TIF-seq data records are shown here. Also, see supplementary figures S4 and S5, Supplementary Material online, for the distribution of all de novo genes and the example of different types of de novo genes. (B) Proximal de novo genes often terminate at the same sites as associated ScANCs. To avoid bias from low-expressing genes, only genes with >40 transcripts in TIF-seq data were analyzed. TSS, transcription start site. TTS, transcription termination site. (C) The upstream type of de novo genes are expressed at higher levels than other types (Mann–Whitney test, P value <2.2e-16 for all pairwise comparisons).