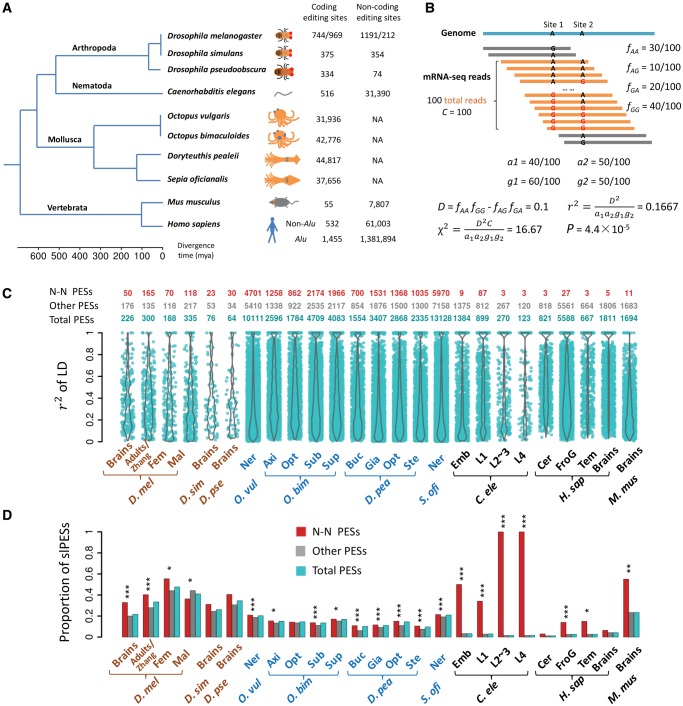
Fig. 1.
The landscape of linkage between RNA editing events in ten metazoan species. (A) A phylogenetic tree of the ten species we used in this study. The numbers of editing sites in coding and noncoding regions are given next to each species. For Drosophila melanogaster, the editing sites before and after the slash were retrieved from brains (Duan et al. 2017) and adults (Zhang et al. 2017), respectively. (B) A hypothetical example of calculating r2 between two editing sites based on the coverage of the NGS reads. Only reads covering the two editing sites (in orange) were included, and the reads spanning only one editing site (in gray) were discarded. (C) Violin plots of r2 (y-axis) for significantly linked PESs in 25 samples of ten species (x-axis). The numbers of total, N–N and the remaining slPESs in each sample are presented above the plots. (D) The proportions of the PESs that have editing events significantly linked in each sample (adjusted P < 0.05). Besides the total PESs, the fraction for the N–N or the remaining PESs that was significantly linked was also calculated in each sample. The fraction of the N–N PESs that is significantly linked was compared with that of the remaining PESs with the Fisher’s exact test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. For the four species O. bimaculoides, D. pealeii, C. elegans, and H. sapiens, only the top four samples with the largest numbers of slPESs are shown in (C) and (D). Fem, female adults; Mal, male adults; Ner, nerve system; Axi, axial nerve cord; Opt, Optic lobe; Sub, subesophageal brain; Sup, supraesophageal brain; Buc, Buccal ganglia; Gia, giant fiber lobe; Ste, stellate ganglion; Emb, embryos; L1, L1 larvae; L2∼3, L2∼3 larvae; L4, L4 larvae; Cer, cerebellum; FroG, frontal gyrus; Tem, temporal lobe. D. mel, Drosophila melanogaster; D. sim, Drosophila simulans; D. pse, Drosophila pseudoobscura; O. vul, Octopus vulgaris; O. bim, Octopus bimaculoides; D. pea, Doryteuthis pealeii; S. ofi, Sepia oficianalis; C. ele, Caenorhabditis elegans; H. sap, Homo sapiens; M. mus, Mus musculus.