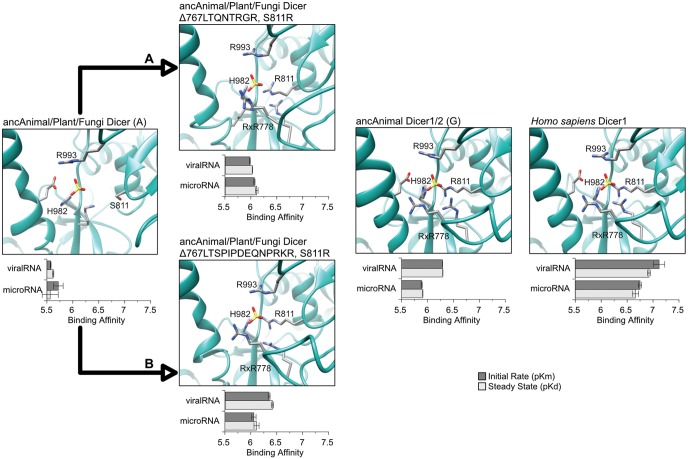
Fig. 5.
Substitutions within the Dicer Platform subdomain increased affinity for viral-like RNA early in animal evolutionary history by forming a conserved 5′ phosphate binding pocket. We measured the binding kinetics of ancestral Platform + PAZ + Connector (PPC) domains to synthetic RNAs modeling microRNAs or viralRNA products (see Materials and Methods; RNA sequences are shown in supplementary fig. S10, Supplementary Material online). We plot steady-state binding (pKd, light bars) and initial binding rates (pKm, dark bars) to each RNA, with longer bars indicating tighter binding. Standard errors are shown, with kinetics curves shown in supplementary fig. S15, Supplementary Material online. We introduced the historical S811R substitution and either short (A) or long (B) animal-specific insertions into the ancAnimal/Plant/Fungi Dicer background (see figs. 2 and 3) and plot the orientations of 5′ phosphate RNA-contact residues by structural homology modeling. Letters in parentheses next to protein names indicate ancestral node identifiers (see fig. 1). Human Dicer1 is shown for comparison.