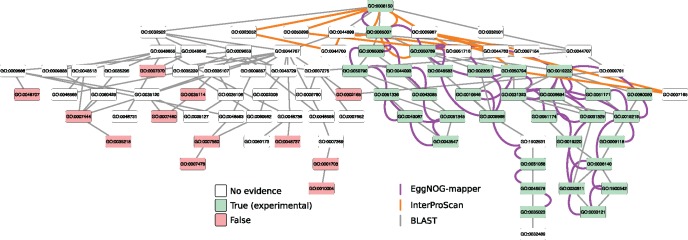
Fig. 4.
Example of eggNOG-mapper, BLAST and interProScan annotations. Example of differential Gene Ontology annotation (Biological Process sub-ontology) for the human protein RHOGAP1 (Rho GTPase activating protein 1, ENSP00000310491) using three alternative methods: BLAST (grey edges), InterProScan (orange), and eggNOG-mapper (purple). The network figure shows the experimentally validated “gold standard” annotations (green nodes), the annotations possible to exclude from taxonomy (red nodes), and annotations neither possible to conclude nor exclude from curated Gene Ontology data (white nodes). All annotations are linked with edges reflecting the Gene Ontology DAG hierarchy. Gray edges connect all GO terms concluded from BLAST analysis, orange edges those concluded from InterProScan, and purple edges those concluded using eggNOG-mapper. Notably, while a BLAST-based approach recovers all curated annotations, in this case it does so at the cost of substantial numbers of false positives and uncertain terms. InterProScan is accurate but obtains only a more general annotation, whereas eggNOG-mapper achieves more detailed resolution.