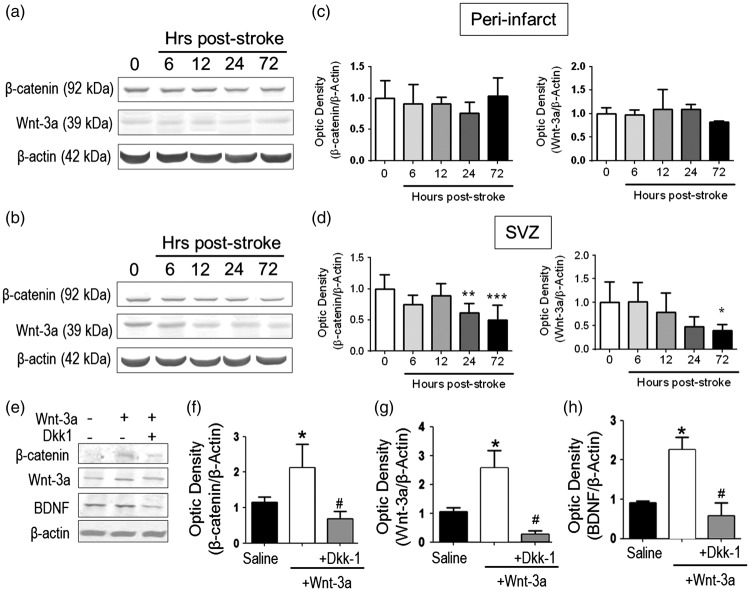
Figure 2.
Wnt-3a supplementation restored Wnt signaling and neurotrophic expression following stroke. (a–d) Endogenous Wnt-3a and β-catenin levels were determined in wildtype animals following stroke by Western blot and densitometry analysis. (a) and (b) Representative Western blot analysis of tissue from the subventricular zone (SVZ, A) and the peri-infarct (b). (c) and (d) In the SVZ (d), β-catenin and Wnt-3a are significantly downregulated during the subacute phase after stroke. No significant differences were observed in the peri-infarct (c). *p < 0.05 compared to hour 0; **p < 0.01 compared to hour 0; ***p < 0.001 compared to hour 0. N = 5 for each group for each timepoint. (e–h). Animals were subjected to focal ischemic stroke and then were given intranasal injections of saline, Wnt-3a, or Wnt-3a + Dkk1. Then, Western blot and densitometry analysis were performed to detect the expression of Wnt-3a, β-catenin and BDNF in peri-infarct regions at 14 days after stroke. Wnt-3a supplementation increased levels of Wnt-3a, its intracellular signaling mediator β-catenin, and the neurotrophin BDNF. All data represented as mean ± SD; *p < 0.05 compared to saline; #p < 0.05 compared to Wnt-3a. N = 7 for saline group, seven for Wnt-3a group, and eight for Wnt-3a + Dkk1 group.