Fig. 1.
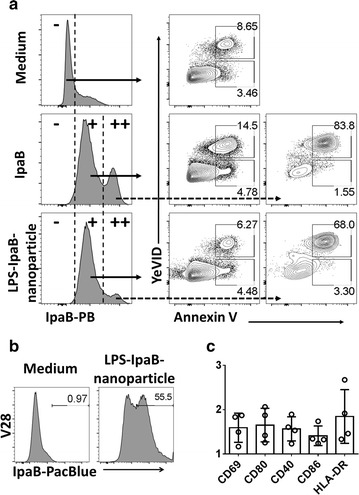
Delivery of IpaB to B-LCL cells by LPS-nanoparticles. a Induction of necrosis/apoptosis in B-LCL by IpaB. Top panels: B-LCL exposed to media for 2 h. Center panels: in B-LCL exposed for 2 h to IpaB (Pacific Blue) two populations were identified (IpaB+ and IpaB++), IpaB+ B-LCL showed an increased in the percentage of cells undergoing necrosis (YeVID+, Anexin V+) (~ twofold compared to media), but no changes in the percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis (YeVID−, Anexin V+). IpaB++ cells showed an important increase in necrosis (~ tenfold compared to media), but not in apoptosis. Bottom panels: in B-LCL exposed for 2 h to to IpaB incorporated into the LPS-nanoparticle (LPS-IpaB-nanoparticles) the same two populations were identified (IpaB+ and IpaB++). However, no induction of necrosis was seen in the IpaB+ population. Also, the IpaB++ population showed a lower degree of necrosis than when exposed to IpaB alone. The data shown is from one representative volunteer of 4 evaluated. b After 18 h of incubation with the LPS-IpaB-nanoparticles, IpaB can be identified in 50–60% of B-LCL and that these cells (c) display upregulation of activation markers. Data in b is from one representative volunteer (#28) and data in c is a composite from four different vaccinees assayed in different days (#39, 24, 30 and 40)
