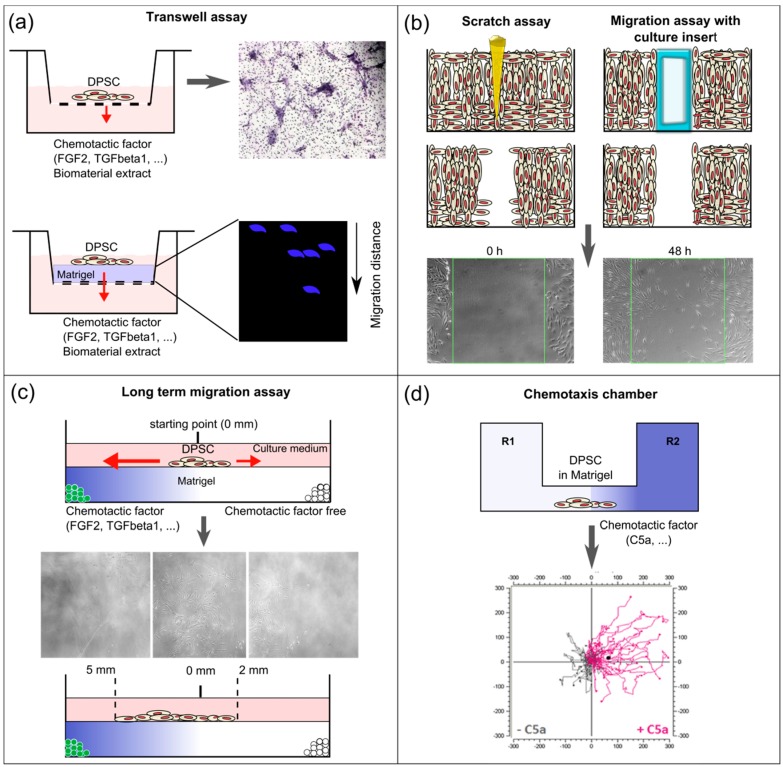
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the different in vitro assays used to study DPSC recruitment and migration. (a) On the upper panel, a classical Trans-well assay used to evaluate the chemotactic potential of bioactive molecules and biomaterials (extracts), with cells seeded on the upper side of the membrane. Results are obtained by swabbing the non-migrated cells from the upper side of the membrane followed by histological staining of the migrated cells on the lower side of the membrane. These can be counted and quantified. On the lower panel, a modified Trans-well assay where the porous membrane is coated with an extracellular matrix (ECM)-like gel (e.g., Matrigel, collagen), on which cells are seeded. Gels can be retrieved to evaluate the migrated distance of cells (e.g., by cell nuclear staining using 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) and confocal microscopy); (b) On the left, scratch assay to evaluate cellular migration. A scratch is made (usually using a pipette point) on confluent cell cultures. On the right, a modified assay to study cellular migration is represented. A culture insert is placed, around which cells are cultured. When the culture is confluent, the insert is removed leaving behind a reproducible cell-free zone with sharp borders, as opposed to the scratch assay. With both techniques, cellular migration into the cell-free zone is followed up microscopically and can be quantified using specialized software. A chemotactic gradient is absent in these assays; (c) Culture model to study long-term migration following the controlled release of chemotactic factors. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres with or without chemotactic factors are embedded in Matrigel in a graduated tissue culture chamber. DPSC are seeded in the middle and their migration can be followed microscopically over long time periods (up to 10 days); (d) Specialized in vitro chemotaxis chamber. A stable chemotactic gradient is established by injecting a solution of chemotactic factor in one of the reservoirs. Cells are seeded in the observation area containing Matrigel in the middle of the chamber. Real-time monitoring of cellular migration can be performed up to 48 h. Quantitative evaluation is carried out by specialized software. Individual cells are tracked and the center of mass (CAM) is calculated. Trajectory plots can be presented graphically.