Fig. 1. General context of the ice-rich area in Juling crater from Framing Camera and VIR spectrometer data.
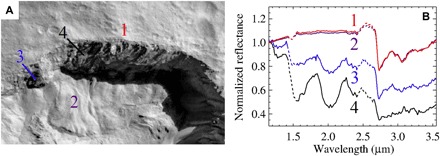
(A) Context Dawn Framing Camera image taken during L1 acquisition of the northern rim of Juling crater. The area in shadow is enhanced to show details of the ice-rich wall. (B) Measured spectra corresponding to positions in (A). Dotted lines represent spectra in the ranges corresponding to instrument filter junctions that could produce fictitious signals. The diagnostic absorption bands of water ice at 1.25, 1.5, and 2.0 μm are visible. The broad absorption band of water ice at 3.0 μm is superimposed to the narrower absorption bands at 2.7, 3.1, and 3.4 μm, which indicates the presence of Mg phyllosilicates, NH4 phyllosilicates, and Mg carbonates (3), respectively. These minerals are ubiquitous on Ceres’ surface (3).
