Fig. 1.
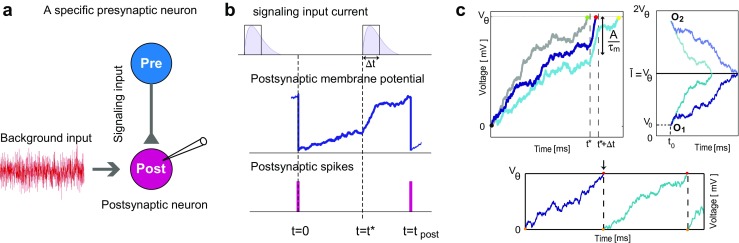
The framework to study the impact of a specified presynaptic neuron on postsynaptic spiking activity. a The effect of specified presynaptic neuron is separated from the noisy background input, which is produced by the rest of presynaptic neurons. b A schematic view of the signaling input activity and its effect on the membrane potential and spiking of the postsynaptic neuron. c Postsynaptic membrane potential versus time, Top-left: There can be different trajectories, due to the noise. Any trajectory, if not reached the threshold before signaling input arrival at t∗, shows a sharp increase during t∗to t∗ + Δt time window. Top-right: For the particular case of , we can use the image method. The membrane potential trajectory and its mirror image coincide at line. This can help to fulfill the thresholding criteria if it is the same line of V = V𝜃. Bottom: It shows the membrane potential trajectory of the postsynaptic neuron. When the voltage reaches to V𝜃, the neuron fires and the voltage resets to 0. Here we particularly consider the first spike after t = 0
