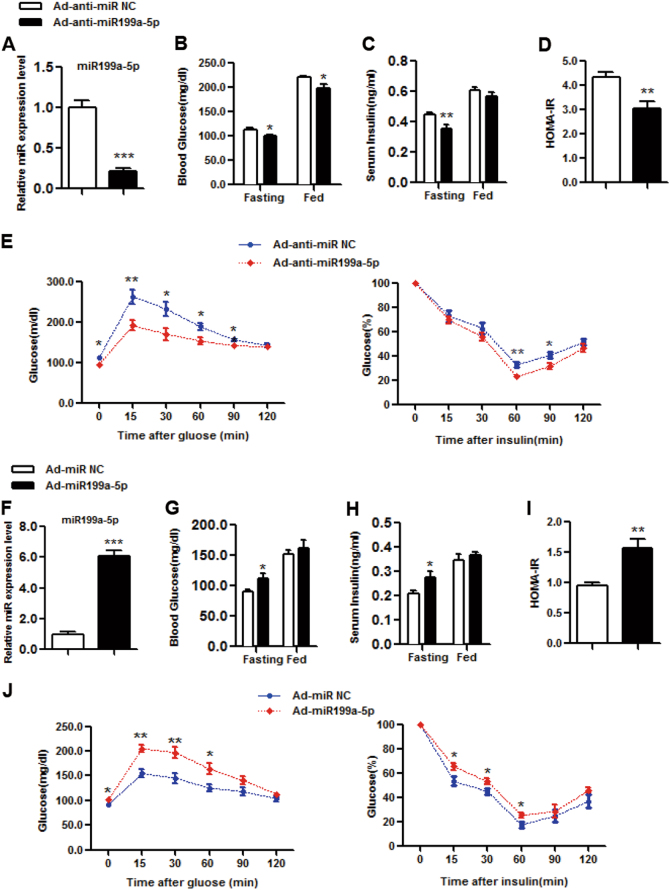
Fig. 2. miR199a-5p regulates insulin sensitivity in vivo.
a-e Male C57BL/6J WT mice were fed a high-fat diet for 3 months and then infected with adenovirus-inhibiting miR199a-5p (Ad-anti-miR199a-5p) or the negative control (Ad-anti-miR NC) via tail vein injection. a Day 9: measurement of hepatic miR199a-5p expression. b, c Days 6 and 5: examination of fed or fasting blood glucose and serum insulin levels. d HOMA-IR index. e Days 5 and 3: performance of GTTs and ITTs. The two-tailed Student's t-test was applied to determine the difference between the group receiving Ad-anti-miR199a-5p and the control group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001), n = 8 mice per group. f–j Male C57BL/6J WT mice fed a chow diet were infected with adenovirus-expressing miR199a-5p (Ad-miR199a-5p) or the negative control (Ad-miR NC) via tail vein injection. f Day 9: measurement of hepatic miR199a-5p expression. g, h Days 6 and 5: examination of fed or fasting blood glucose and serum insulin levels. i HOMA-IR index. j Days 5 and 3: performance of GTTs and ITTs. The two-tailed Student's t-test was applied to determine the difference between the Ad-miR199a-5p group and the control group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001), n = 6 mice per group