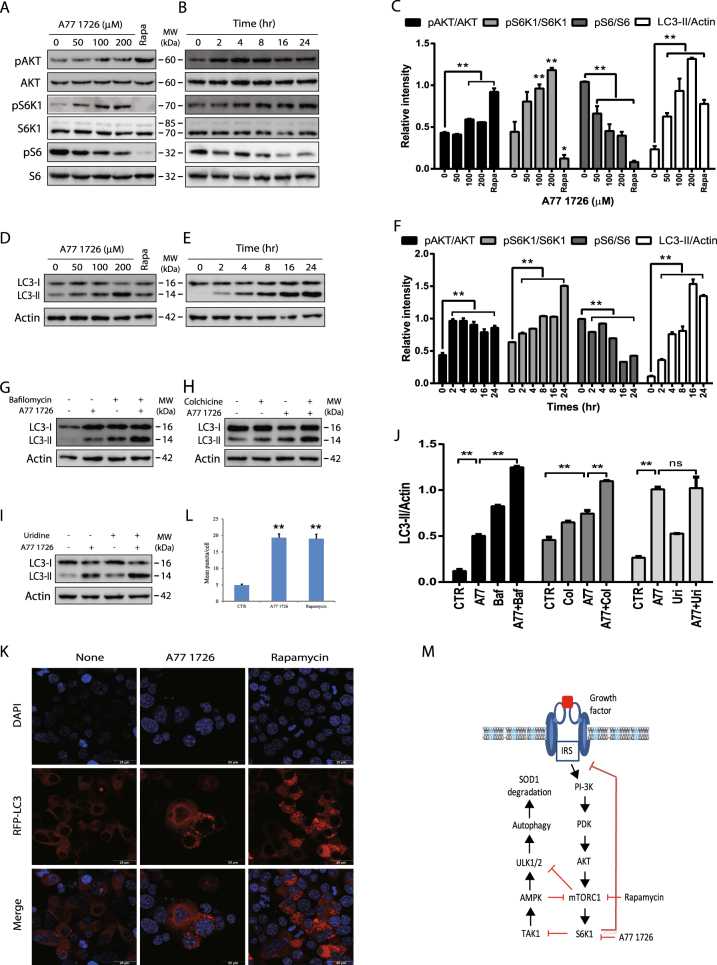
Fig. 1. The effect of A77 1726 on the feedback activation of the PI-3 kinase pathway and autophagy.
a–f The effect of A77 1726 on the feedback activation of the PI-3 kinase pathway and LC3-II lipidation. NSC34 cells were incubated in complete DMEM medium in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of A77 1726 for 16 h (a, c, d) or were incubated in the presence of A77 1726 (200 μM) for the indicated time (b, e, f). Rapamycin (50 nM) was included as a positive control (a, d, c). Cell lysates were analyzed for the feedback activation of the PI-3 kinase pathway (a, b) or for LC3-II lipidation (c, d) by western blot with the indicated antibodies. g, h The effect of bafilomycin and colchicine on LC3-II lipidation. NSC34 cells were incubated in complete DMEM medium in the absence or presence of A77 1726 (200 μM) minus or plus bafilomycin (100 nM) (g, j) or colchicine (5 μM) (h, j) for 16 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for LC3 and actin expression by western blot. i, j Inability of uridine to block A77 1726-induced LC3-II lipidation. NSC34 cells were incubated in complete DMEM medium in the absence or presence of A77 1726 (200 μM) minus or plus uridine (200 μM) for 16 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for LC3-II lipidation and actin expression by western blot. The expression levels were analyzed by quantification of the density of the protein bands with NIH Image-J software and presented as bar graphs (c, f, j). LC3 lipidation was analyzed by comparing the density of LC3-II with β-actin. The data in Fig. 1c, f, j and the remaining Image-J-derived data in all other figures are the mean ± SD from three experiments. k, l NSC34 cells were transfected with the expression vector pmLC3-RFP. The cells were left untreated or treated with A77 1726 (200 μM) or rapamycin (50 nM) for 16 h. Autophagosomes were visualized under a confocal microscope (k). The puncta of autophagosomes were counted under a fluorescent microscope and plotted in a bar graph with statistical analysis (l). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. m Schematic model of A77 1726-induced autophagy. Inhibition of S6K1 activity leads to TAK1 activation, which activates AMPK. AMPK phosphorylates ULK1S555 and activates it. Inhibition of S6K1 by A77 1726 leads to the feedback activation of the PI-3 kinase pathway, as evidenced by increased AKT and S6K1 phosphorylation. Rapamycin also induces the feedback activation of the PI-3 kinase pathway. However, rapamycin targets mTOR, leading to decreased S6K1 phosphorylation