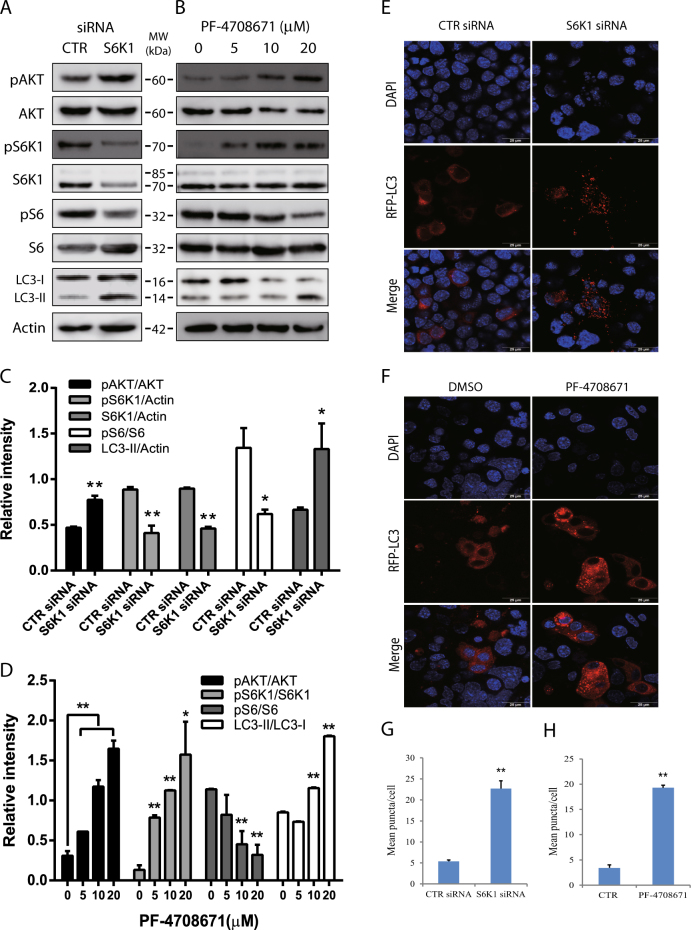
Fig. 2. S6K1 inhibition induces autophagy.
a, c The effect of S6K1 knockdown on LC3-II lipidation. NSC34 cells were transfected with scrambled or S6K1 siRNA (2.5 nmole each). After incubation for 48 h, cell lysates were prepared and analyzed for total and phosphorylated proteins by western blot. b, d The effect of the S6K1 inhibitor on LC3-II expression. NSC34 cells seeded in 6-well plates were incubated in complete DMEM medium in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of PF-4708671 for 16 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for total and phosphorylated proteins by western blot. The expression levels were analyzed by quantification of the density of the protein bands with NIH Image-J software and presented as bar graphs (c, d). e The effect of S6K1 knockdown on autophagosome formation. NSC34 cells seeded on the coverslips were first transfected with scrambled or S6K1 siRNA (2.5 nmole each). After incubation overnight, the cells were transfected with pmLC3-RFP expression vector. After incubation for 48 h, the cells were fixed in methanol and visualized for autophagosomes under a confocal fluorescent microscope. f The effect of the S6K1 inhibitor on LC3-II expression. NSC34 cells seeded on coverslips were transfected with LC3-RFP expression vector. After incubation for 24 h, the cells were treated with DMSO (0.2%) or PF-4708671 (20 μM) for 16 h. Cells were fixed and analyzed for autophagosomes under a fluorescent microscope. g, h The puncta of autophagosomes were counted under a fluorescent microscope and plotted in a bar graph with statistical analysis. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01