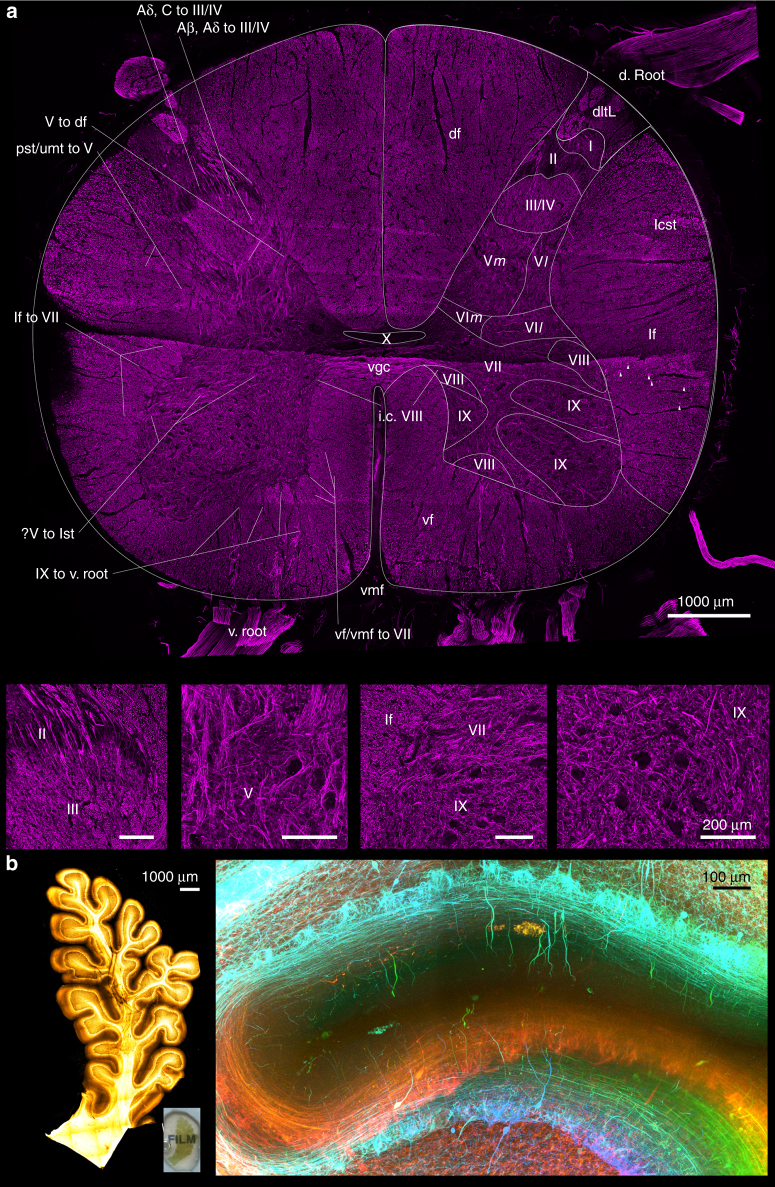
Fig. 3.
Application of 3D immunohistochemistry with next-generation histology. a Maximum intensity projection image of a 9.5 mm-wide, 8.1 mm-tall, 2 mm-thick spinal cord block stained for neurofilament (imaging Z-depth = 462.60 µm). Magnified view of different laminae was shown in lower images (Scale bars = 200 µm). Roman numerals from I to X: laminae of Rexed, where the suffix m and l denotes the medial and lateral divisions, respectively. Aβ, Aδ to III/IV Aβ-type and Aδ-type input fibres from dorsolateral tract to lamina III/IV, Aβ, C to III/IV Aβ-type and C-type input fibres from dorsolateral tract to lamina III and IV of Rexed, df dorsal funiculus, d. root dorsal root, i.c. VIII interconnecting fibres between bilateral laminae VIII of Rexed, IX to v. root: output motor fibres from lamina IX of Rexed to ventral root, lcst lateral corticospinal tract, lf lateral funiculus, lf to VII lateral funiculus fibres input into the lamina VII of Rexed, pst/umt to V propriospinal tracts or upper modulating tracts input into the lamina V of Rexed, v. root ventral root, ?V to lst fibres from the lamina V of Rexed on the right side coursing through the grey matter to form the lateral spinothalamic tract of the left sid, V to df output tracts from lamina V of Rexed into the dorsal funiculus, vf ventral funiculus, vf/vmf to VII input fibres from the ventral funiculus or ventromedial funiculus into the lamina VII of Rexed, vgc ventral grey commissure, vmf ventral median fissureb. A block of 17.6 mm-wide, 9.5 mm-tall, 1.5 mm-thick formalin-fixed cerebellar folium delipidated with SDS for 3.5 months, immunostained for neurofilament, and cleared with OPTIClear. The inset shows the gross appearance of the folium. Overview of immunostaining (right) and detailed view demonstrated by colour depth-coded image (below; Z-depth = 546.00 µm) from the white boxed area on the right.