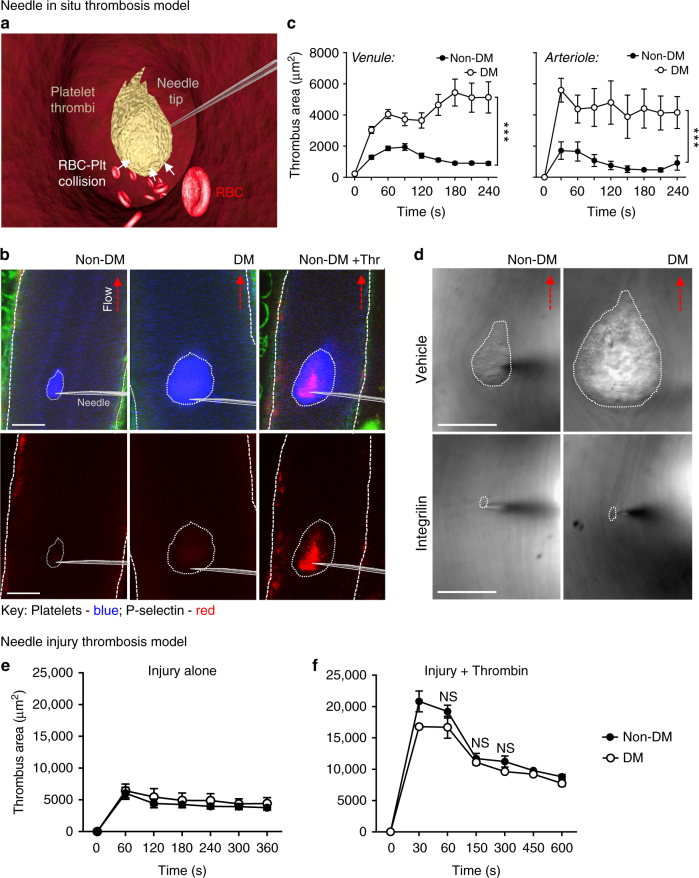
Fig. 1.
Diabetes exaggerates discoid platelet thrombus growth under local flow disturbance in vivo. Control non-diabetic (non-DM) and diabetic (DM) mice were administered Dylight 649-anti-GPIbβ Ab and Alexa 546-anti-P-selectin Ab, prior to subjection to the ‘needle in situ’ model of thrombosis, as described under ‘Methods section’. In some experiments (d), mice were treated with vehicle or integrilin (as described) prior to needle injury. a Schematic illustration of the ‘needle in situ’ thrombosis model, wherein a microinjector needle is inserted into the center of the vessel lumen to create local flow disturbance. Thrombus formation is initiated at the needle tip and propagated by aggregating discoid platelets. Red blood cells (RBCs) have a collisional effect on platelets within the growing thrombus. b Thrombus growth (blue) and P-selectin expression (red) were monitored in real-time via confocal microscopy, with representative images depicting P-selectin−ve thrombi (blue) in both non-DM and DM mice, 4 min post-needle insertion. P-selectin+ve thrombi were detected only following injection of thrombin (green: collagen autofluorescence). c, d Thrombus surface area of non-DM and DM mice was quantified at the indicated time points post-needle insertion. c Results are expressed as mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 mice (6–8 thrombi per mouse examined in venules and 5 thrombi per mouse in arterioles). d Representative DIC images depicting thrombi (dotted line) forming 4 min post-needle insertion in non-DM and DM mice, either untreated (control) or treated with αIIbβ3 antagonist integrilin (4 mg kg−1, i.v.). e, f In some experiments, thrombi induced in non-DM and DM mice by needle perturbing mesenteric venules alone (e) was compared to local injection of thrombin (100 U mL−1) (f). Thrombus formation was monitored using DIC intravital microscopy and thrombus surface area quantified at the indicated injury times. Results (e, f) are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3 mice, (2–3 thrombi per mouse). For all studies, results were assessed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test, where *p < 0.5; ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars = 50 μm