Figure 3.
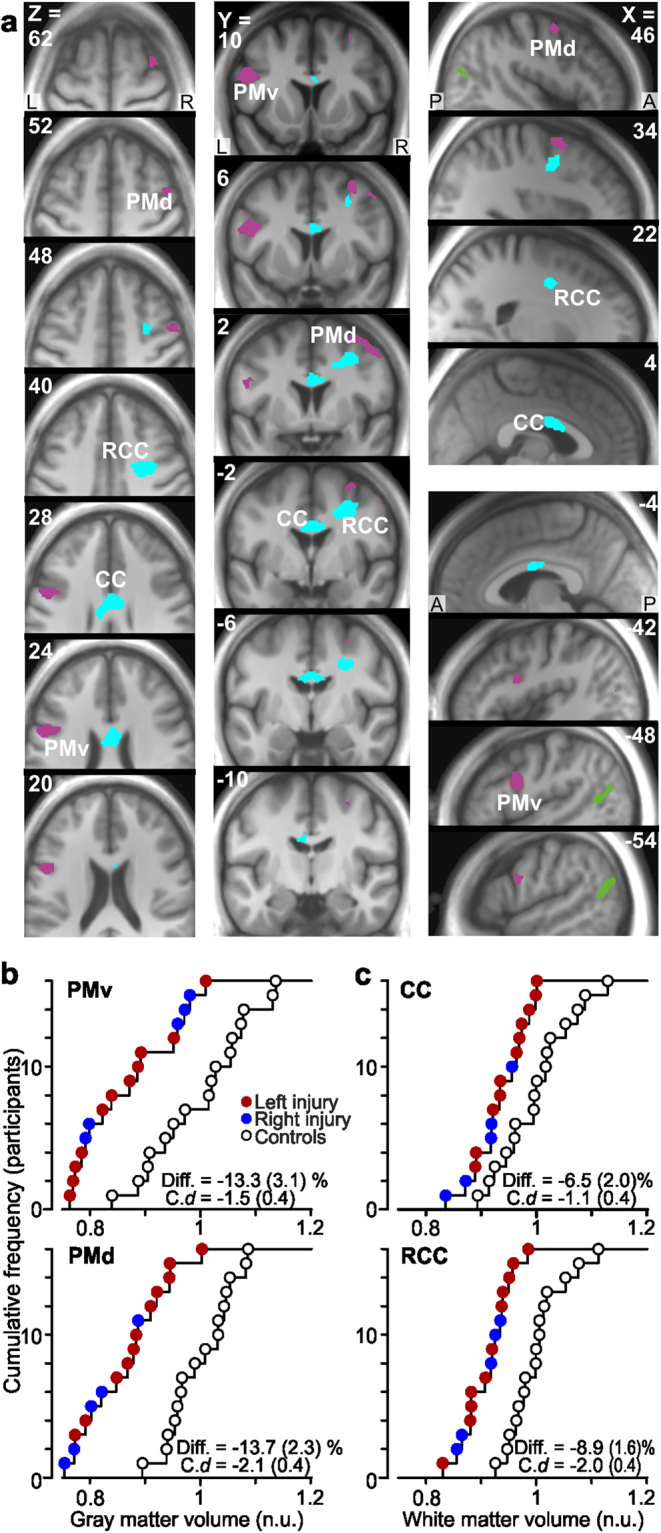
Reduced gray and white matter volume in premotor areas of median nerve-injured participants. (a) Areas with reduced gray (magenta) and white (cyan) matter volume as compared to control participants shown on axial, coronal and sagittal slices. (Green areas indicate extrastriate visual areas with increased gray matter volume). For the gray matter, one cluster (206 voxels) with a single local maximum (−48, 6, 26: Ze = 3.8) was located in the ventral premotor cortex (PMv) of the left hemisphere and one cluster (207 voxels) showing three local maxima (34, 2, 62: Ze = 3.6; 46, 2, 52: Ze = 3.0; 30, −12, 56: Ze = 2.7) was located in the dorsal premotor cortex (PMd) of the right hemisphere. For the white matter one cluster (276 voxels) with two local maxima (6, 0, 28: Ze = 3.1; −6, -8, 26: Ze = 3.0) was located in the mid-body of corpus callosum (CC) and one cluster (301 voxels) with a single maximum (32, 0, 40: Ze = 4.3) was located in the white matter beneath the right PMD radiating from corpus callosum (RCC). R, right; L, left; A, anterior; P, posterior. (b) and (c). Distribution of gray matter volume in the detected zones in left PMv and right PMd, and white matter volume in CC and RCC (from areas in a) among the nerve-injured participants (red and blue filled circles) and the control participants (black open circles). For further details, see legend of Fig. 2.
