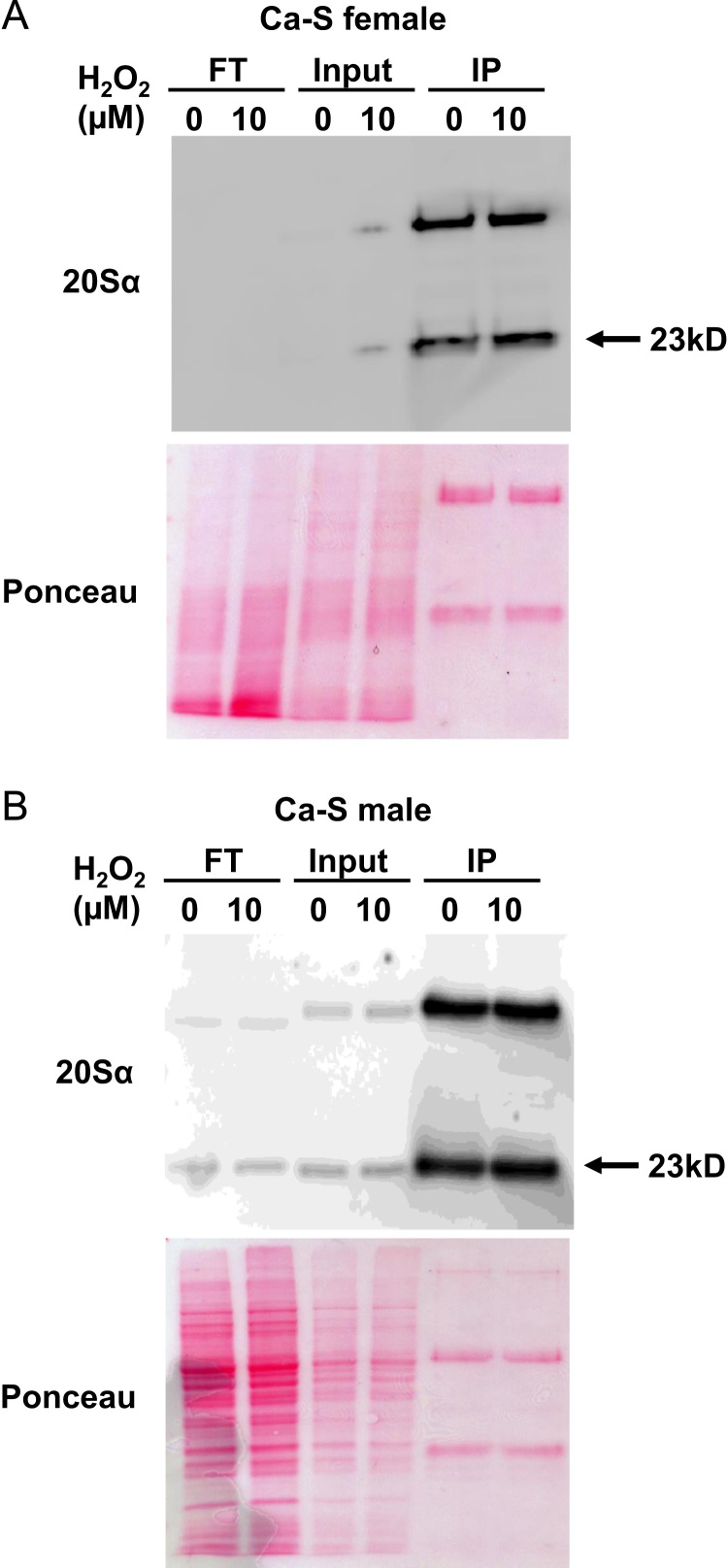
Fig. 2.
Immunoprecipitation of the proteasome Female and male progeny of the Ca-S strain were either untreated, or were pretreated with 10 µM H2O2 as per Section 2, above. Afterwards, whole fly lysates underwent immunoprecipitation (IP) against the 20S proteasome α subunit D. melanogaster specific monoclonal antibody, with a small portion (not utilized in the IP) reserved for the input. Panel A shows a Western blot (upper gel) of flow-through (FT), input, and IP against the 20Sα subunit for female flies, with a Ponceau stained lower gel, and Panel B reports the results of the same procedures for male flies. Ponceau staining, which is a reversible method to detect protein bands on PVDF membranes, as an assessment of protein loading between treatment groups. The amount of 20S proteasome α subunit present in each lysate was assessed by three stages on the western blot: flow-through (FT), input, and IP against the 20Sα subunit. The flow-through (FT) was to assess the IP efficiency: a means to measure how much of the 20Sα subunit was not pulled out from the lysate, with the lower the density, indicating higher IP efficiency by the antibody. The input assessed how much 20Sα subunit was present in lysate collected following no pretreatment (0 µM H2O2) or pretreatment (10 µM H2O2). The IP was the amount of the 20S proteasome α subunit detected when the monoclonal antibody against the 20S α subunit was added to the lysate to ‘pull out’ the 20S proteasome and enable detection of protein amount.