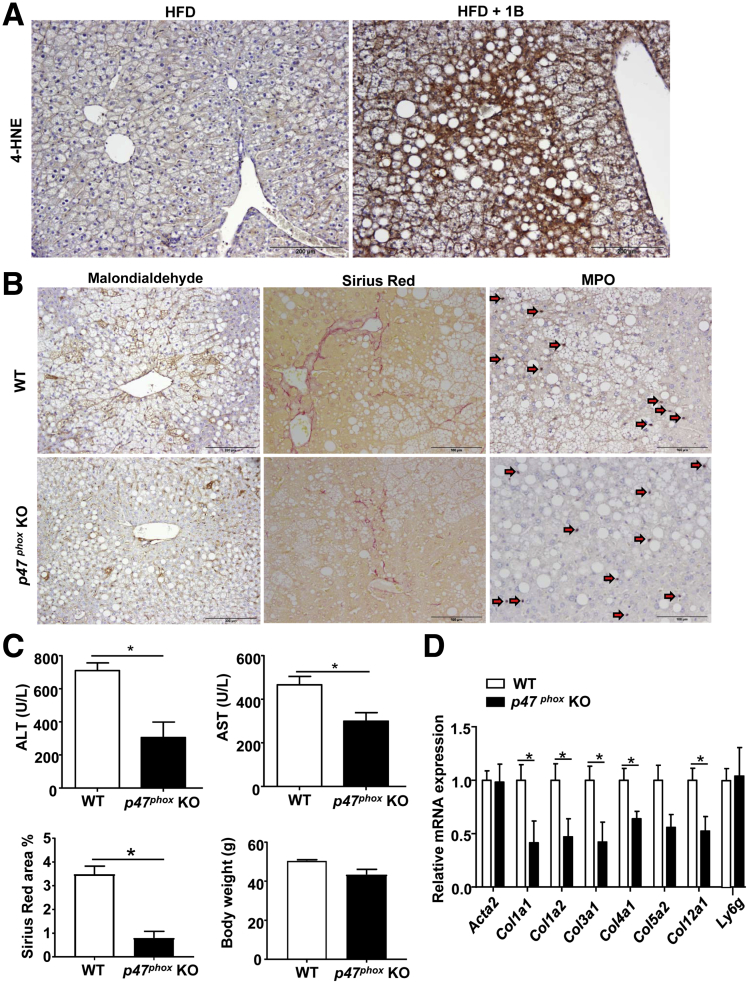
Figure 6.
P47phoxKO mice have reduced liver damage and fibrosis in the HFD+1B ethanol model. (A) C57BL/6J mice were subject to HFD+1B ethanol or HFD-plus-maltose (HFD group) challenge. Liver tissues were collected and subject to 4-HNE staining. (B–D) WT and p47phox KO mice were subject to HFD+1B ethanol challenge. Malondialdehyde Sirius Red, and MPO staining were performed on the liver tissue sections. (B) Representative images are shown, arrows indicate MPO+ cells). (C) Serum ALT and AST levels, percentage of Sirius Red–positive area, as well as body weight were measured. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of liver fibrosis-related genes and Ly6g mRNA. N = 4–7 in each group, *P < .05.