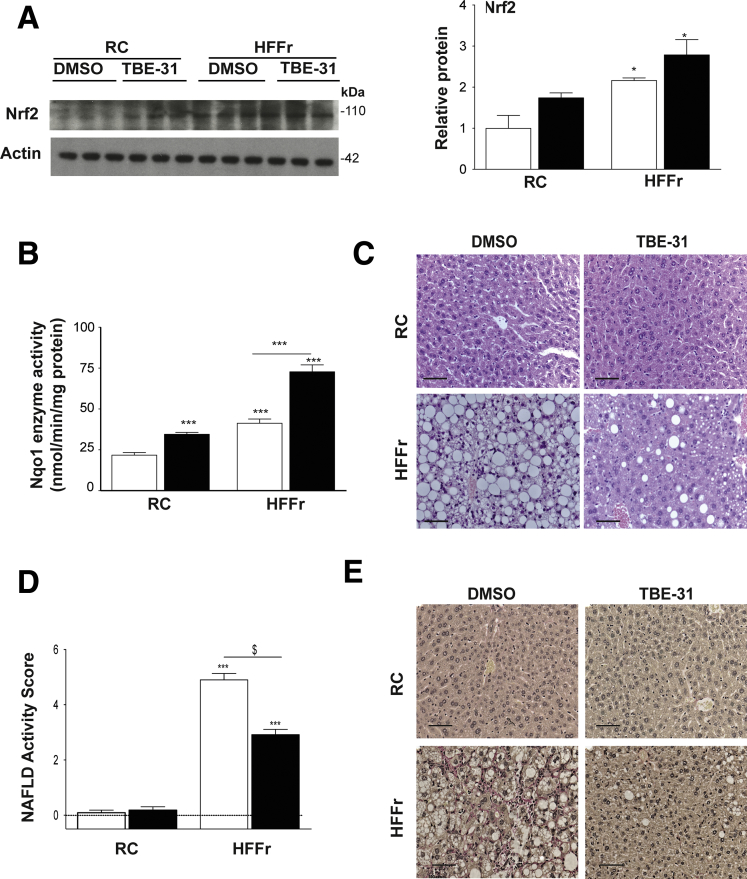
Figure 6.
TBE-31 treatment increases hepatic Nrf2 activity and improves liver histology in HFFr-fed Nrf2+/+mice. On completion of the Study 1 protocol, Nrf2+/+ mice were killed and livers removed. (A) A representative immunoblot for Nrf2 protein in liver extracts from RC-fed or HFFr-fed mice treated with DMSO or TBE-31 (left side), with densitometric scans of blots (right side) (n = 6 biologic replicates). (B) Nqo1 catalytic activity in hepatic extracts from RC-fed and HFFr-fed mice (n = 8–12 mice per group). (C) Representative images for H&E staining of liver sections from RC- and HFFr-fed Nrf2+/+ mice treated with DMSO or TBE-31 (scale bars = 100 μm). (D) The NAFLD activity score39 was calculated (n = 8–12 mice per group): note, on the y-axis the score includes negative values because livers from RC-fed Nrf2+/+ mice gave NAFLD activity scores of essentially zero. (E) Representative images for van Gieson staining of liver sections from Nrf2+/+ mice after 30 weeks RC or HF55Fr/HF30Fr feeding, followed by 6 weeks DMSO or TBE-31 treatment (scale bars = 100 μm). White bars, DMSO treated; black bars, TBE-31 treated. Results are means ± SEM. Significant increases in Nrf2 protein, Nqo1 activity, or NAFLD activity score, relative to that in livers from RC-fed Nrf2+/+ mice, are indicated by: *P < .05; ***P < .001. Significant decreases in NAFLD activity score upon treatment with TBE-31, relative to HFFr-fed Nrf2+/+ mice, are indicated by: $P < .05.