Figure EV1. Comparison of wild‐type and template‐free (TF) telomerase reconstitution systems.
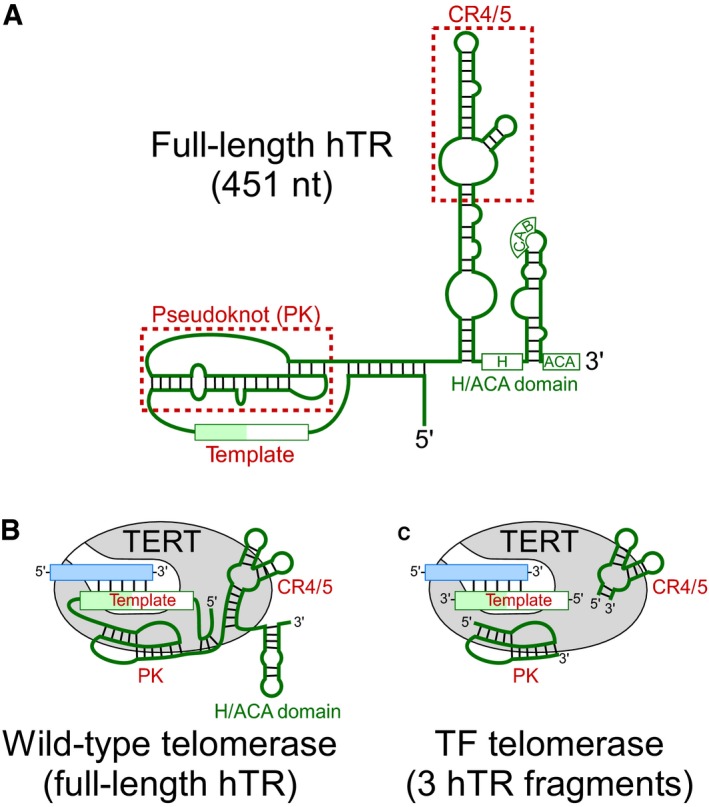
- Schematic of the 451‐nt full‐length hTR. The hTR secondary structure comprises three major structural domains: the pseudoknot (PK), conserved regions 4/5 (CR4/5), and box H/ACA domain. The template region and the two structural domains, PK, and CR4/5 (red), are minimally required for reconstituting telomerase activity in vitro.
- The wild‐type telomerase core enzyme comprises the full‐length hTR (green) and the catalytic TERT protein (gray). The substrate for wild‐type telomerase is a single‐stranded DNA primer (blue).
- TF telomerase comprises the minimally required PK and CR4/5 hTR fragments (green). The substrate for TF telomerase is duplex of a single‐stranded DNA primer (blue) pre‐annealed with an RNA template.
