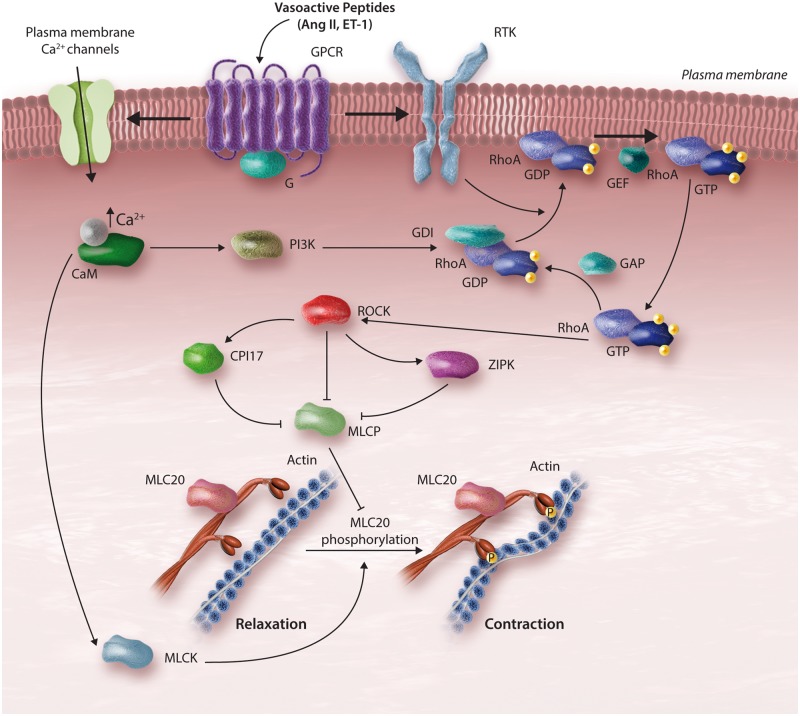
Figure 2.
ROCK-induced contraction of VSMCs. Vasoactive agents bind to their respective GPCRs leading to release of RhoA from a guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI). RhoA translocates to the membrane. Mechanisms involving RhoA activation also involve transactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). GEFs promote exchange of Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to Guanosine triphosphate (GTP), activating the RhoA-ROCK pathway. Activated ROCK renders MLCP inactive by phosphorylation of CPI-17 and/or zipper-interacting protein (ZIPK), facilitating MLC20 phosphorylation and vascular contraction. Increased Ca2+ may directly activate ROCK through phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent pathways.