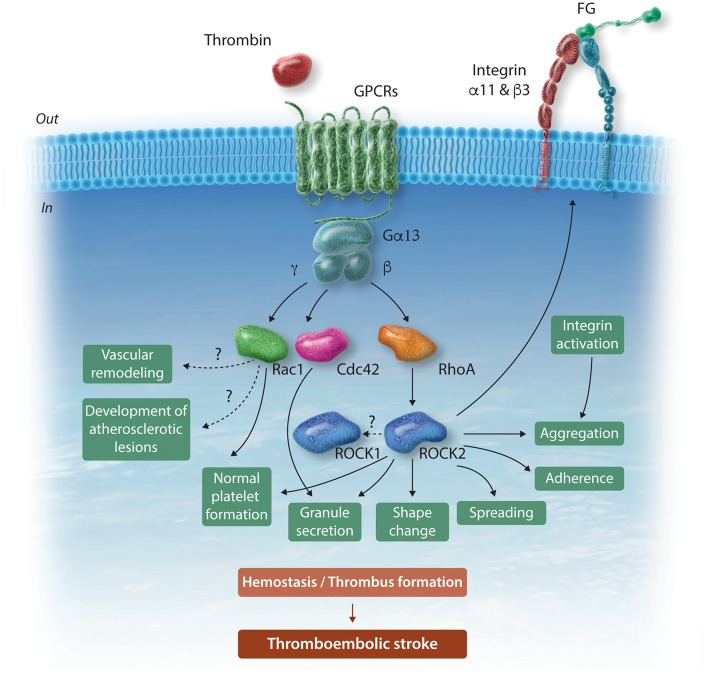
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of ROCK2 signalling in platelets, underlying haemostasis, thrombus formation and thromboembolic stroke. Thrombin and other platelet agonists through GPCRs induce RhoA-mediated activation of ROCK2. ROCK2 drives separate steps of platelet activation, leading to thrombus formation and ultimately to thromboembolic stroke. ROCK2 also regulates platelet formation by megakaryocytes albeit to a considerably lesser degree than Rac1 or Cdc42. For the sake of simplicity, RhoA (and possibly ROCK2)-driven platelet contraction and clot retraction are not shown. Intriguingly, platelet-selective deletion of ROCK2 does not affect vascular remodelling and atherogenesis. Cdc42, cell division control protein 42 homolog (Rho-type GTPase); FG, fibrinogen; GPCRs, G-protein-coupled receptors; Gα13, β, γ, G-protein subunits coupling to GPCRs; Rac1, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rho-type GTPase); RhoA, Ras homolog gene family member A; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinase.