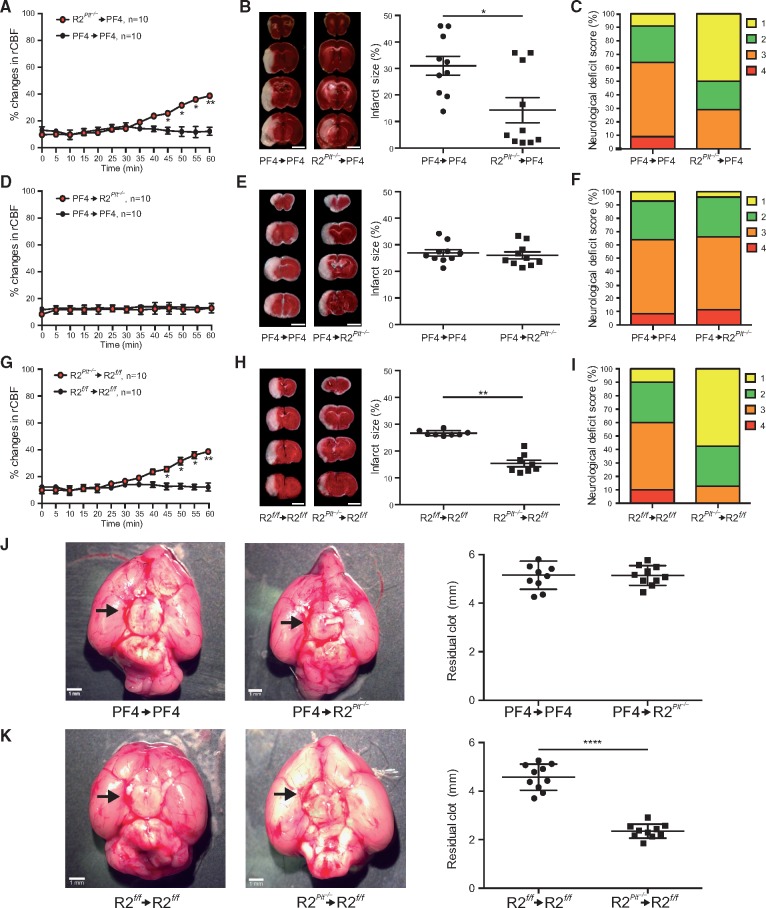
Figure 4.
Neuroprotective effects of platelet ROCK2 deficiency in thromboembolic stroke. Pre-formed clots from control (PF4-Cre) or ROCK2Plt−/− mice were injected into the middle cerebral artery of recipient PF4-Cre mice with corresponding (A) percent change in relative cerebral blood flow, (B) coronal brain sections stained with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) (left panel, scale bar 5 mm) and cerebral infarct volume (right panel), and (C) neurological deficit score (n = 10). Pre-formed clots from control (PF4-Cre) mice were injected into the middle cerebral artery of recipient PF4-Cre or ROCK2Plt−/− mice with corresponding (D) percent change in relative cerebral blood flow, (E) coronal brain sections stained with (TTC) (left panel) and cerebral infarct volume (right panel), and (F) neurological deficit score (n = 10). Pre-formed clots from control (ROCK2fl°x/fl°x) or ROCK2Plt−/− mice were injected into the middle cerebral artery of recipient ROCK2fl°x/fl°x mice with corresponding (G) percent change in relative cerebral blood flow, (H) coronal brain sections stained with TTC (left panel) and cerebral infarct volume (right panel), and (I) neurological deficit score (n = 10). (J) and (K) Residual clot size after thromboembolic stroke (n = 10). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. All data are expressed as mean±SEM.