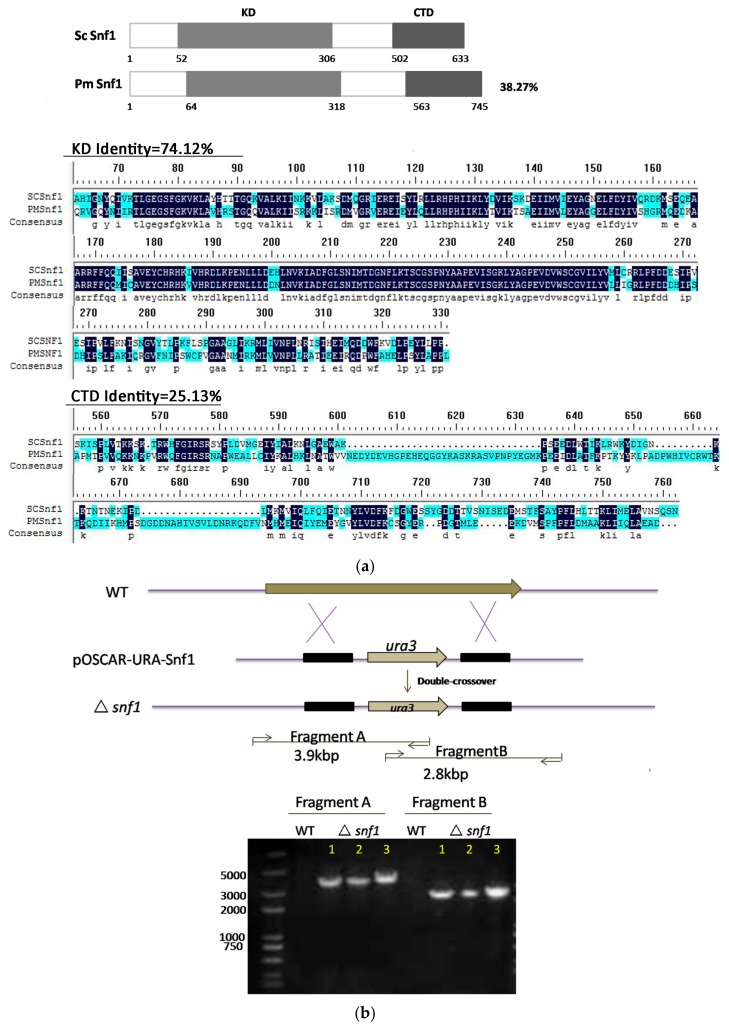
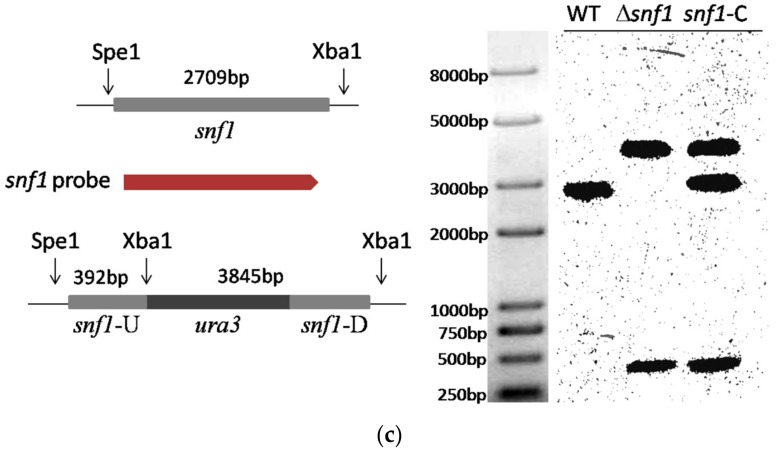
Figure 1.
Identification and deletion of snf1 in Pestalotiopsis microspora NK17. (a) Schematic diagram of the structure of Snf1 protein from P. microspora NK17 and amino-acid sequence (partial sequence) alignments of Snf1 homologs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Numbers indicate the length and the location of the conserved domain of the protein, including kinase domain (KD) and C-terminal domain (CTD). The overall percentage of amino acid sequence identity with ScSnf1 is shown on the right. The identical amino acids are starred and highlighted in blue and the less conserved amino acids are shown in turquoise; (b) The disruption cassette on the vector pOSCAR-URA-Snf1 carried the homologous fragments of snf1. Bottom panel showed the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) verification of the deletion in the mutants. Two fragments, 3.9 kb and 2.8 kb, were obtained by PCR amplification for Δsnf1, while no band was seen for NK17; (c) The left panel, the wild-type copy that was reintroduced in the deleted strain Δsnf1 was shown. And the probe used in Southern blotting (the right panel) was highlighted in red. Southern blot was shown on the right to confirm the deletion of snf1. Genomic DNAs from NK17, Δsnf1 and the complementation strain snf1-C were digested with Spe I and Xba I. The probe used for Southern blotting was amplified by primers Snf1-up (F) and Snf1-down (R). Two bands on the membrane, at 0.4 and 3.8 kb, were obtained for Δsnf1, while in wild-type (WT) NK17, one band of 2.7 kb was observed. In the complementation strain snf1-C, there were three bands (0.4, 2.7 and 3.8 kb).